Every day, you handle sensitive data that could expose your organization to serious risks if compromised. Protecting this information isn’t optional anymore; it’s a business necessity with direct financial and reputational consequences. The number of scam encounters where U.S. individuals shared PII rose by 43% in 2025 compared to the previous year. You face growing threats from phishing, social engineering, and data misuse that can damage trust and disrupt operations. You need clarity on what qualifies as PII, how it’s exploited, and the right ways to protect it. Understanding PII's meaning is your first step toward stronger security.
Key Takeaways
- PII (Personally Identifiable Information) includes data like names, emails, and phone numbers that can identify individuals. It’s vital to protect this data to avoid security risks.
- PII is classified into direct identifiers (e.g., Social Security numbers) and indirect identifiers (e.g., IP addresses). Sensitive PII can lead to identity theft, while non-sensitive data poses less immediate risk.
- Sensitive PII becomes more dangerous when combined with other data, such as linking a name with a birthdate or location, making it easier to identify a person.
- Common PII theft methods include phishing, malware attacks, and social engineering.
- Businesses must implement data safeguards like encryption, access control, and regular audits to mitigate risks.
What is PII?
Personally Identifiable Information, or PII, is the customer data you collect—names, emails, phone numbers, even device or location details. It’s what helps you personalize campaigns, track performance, and understand audience behavior across channels. But this same information can quickly become a liability if misused or exposed. When you understand what qualifies as PII, you can build smarter, privacy-compliant marketing strategies that protect both your customers and your brand.
To fully understand how to handle PII effectively, it's important to examine the different types of data you may encounter.
Types of Personally Identifiable Information
Personally Identifiable Information (PII) falls into two main types based on how easily it identifies someone. Understanding this helps you manage data more effectively and apply the right level of protection. Here’s how PII is typically categorized:
| Type | Description | Examples |
| Direct Identifiers | Data that can identify a person immediately without any additional information. | Full nameSocial Security NumberE-mail addressphone numberpassport number |
| Indirect Identifiers | Data that may not identify someone on its own, but can do so when combined with other details. | Location dataIP addressBrowser cookiesDevice IDs, ZIP code |
Once you've grasped the two main categories of PII, it’s also important to differentiate between sensitive and non-sensitive information.
Also read: Understanding Steps in Achieving Privacy-First Marketing
Sensitive PII vs Non-Sensitive PII
Not all personal data carries the same level of risk; some details can cause serious harm if leaked, while others are less damaging. Knowing this difference helps you prioritize which information needs the highest level of protection in your marketing systems. Here are the two main categories:
1. Sensitive PII
Sensitive PII refers to information that, if exposed, can directly lead to identity theft, fraud, or other serious harm. This includes Social Security numbers, passport details, financial records, medical history, and biometric data. If compromised, sensitive PII can trigger legal liabilities, regulatory penalties, and permanent loss of customer trust, especially for brands operating in regions with strict privacy laws.
2. Non-Sensitive PII
Non-sensitive PII includes data that can identify a person but generally poses a lower immediate risk if leaked. Examples include first names, ZIP codes, or business email addresses used for professional communication.
Let’s take a look at situations where sensitive information can evolve into PII through context and combination with other data.
When Does Sensitive Information Become PII?
Some information may seem harmless on its own, but can become personally identifiable when combined with other data points. Here are common examples of when sensitive information transforms into PII:

- Combination of Basic Details: A birthdate or ZIP code alone may seem harmless, but when paired with a full name or email, it can uniquely identify an individual. For example, combining “John Smith” with ZIP 90210 and birthdate 01/15/1985 can pinpoint a single person.
- Behavioral and Location Data: IP addresses, browsing history, or GPS data can reveal identities when linked to account information or purchase activity. For example, tracking a user’s IP and visited product pages can expose their buying patterns and identity.
- Device and Account Identifiers: Device IDs, login usernames, or cookies may not identify someone directly, but become PII when connected to demographic or transaction data. For example, linking a mobile device ID to an app account can reveal the user’s personal information.
- Contextual Linking: Even non-sensitive information, like generic survey responses or subscription preferences, can become identifying if cross-referenced with other datasets. For example, survey answers combined with email lists can identify specific customers.
With an understanding of when sensitive data can become PII, let’s examine some of the methods often used to steal this information and put businesses at risk.
Common Methods of PII Theft
PII theft can disrupt campaigns, damage customer trust, and even trigger compliance penalties if your data isn’t protected. Here are the main methods by which PII is commonly stolen:
- Phishing: Attackers send fake emails or messages to trick you into revealing customer login credentials or marketing account access. Example: A spoofed client request prompts your team to provide campaign reporting details, exposing sensitive PII.
- Malware Attacks: Malicious software infects devices or servers to capture stored PII or analytics data. Example: Downloading an unverified plugin for your marketing dashboard installs a keylogger that steals customer email lists.
- Social Engineering: Scammers manipulate your team or clients to share sensitive information. Example: An impostor posing as a vendor convinces an employee to disclose campaign tracking IDs or client contact info.
- Insider Threats: Employees or contractors accidentally or intentionally expose customer data while managing campaigns or e-commerce systems. Example: A contractor exports client data from a CDP to a personal device without authorization.
Now that you’re aware of the risks, let’s look into the steps you can take to secure this data across your operations.
Also read: Navigating Attribution in a Cookieless and Privacy-First World: A Comparative Analysis
How to Safeguard Personally Identifiable Information?
Safeguarding PII is critical when your campaigns rely heavily on customer data across multiple platforms and channels. Here are key strategies to protect sensitive information:
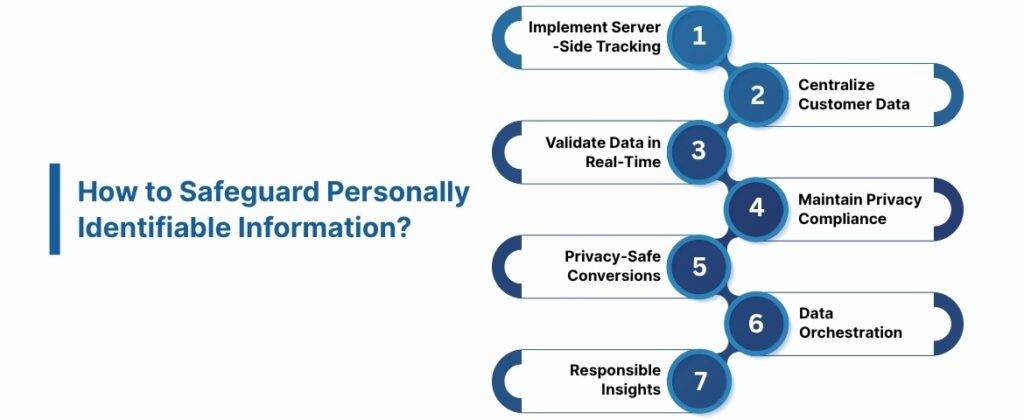
1. Implement Server-Side Tracking
Shifting tracking from the browser to the server reduces exposure to third-party breaches and ad-blockers while ensuring accurate data capture. For example, tracking customer behavior server-side allows you to collect conversion signals without compromising privacy. Ingest IQ enables server-side tracking to accurately capture customer signals while managing multi-channel data securely and privacy-compliantly.
2. Centralize Customer Data
Unifying data from multiple sources helps you maintain consistent records, reduces duplication, and allows better control over sensitive information. For instance, integrating CRM and e-commerce data creates a single source of truth for marketing decisions. Ingest ID provides a first-party identifier for each visitor, centralizing customer data for real-time segmentation and personalized engagement.
3. Monitor and Validate Data in Real-Time
Constant monitoring ensures that tracking tags and data pipelines function correctly, minimizing errors and potential leaks. For example, live debugging of web and mobile tags helps spot anomalies before they affect campaigns. Ingest IQ offers real-time tag monitoring and data streaming to CDPs or data lakes, safeguarding accuracy and completeness.
4. Maintain Privacy Compliance
Complying with GDPR, CCPA, and other global regulations prevents legal penalties and builds customer trust. For example, managing consent preferences ensures that you collect only authorized information from users. Event IQ supports privacy compliance by managing customer consent and implementing ethical data practices across marketing workflows.
5. Optimize Conversions Without Compromising Privacy
Enhancing conversions while respecting privacy allows you to personalize experiences safely, reduce cart abandonment, and drive ROI. For instance, tracking high-value actions without storing unnecessary PII improves campaign efficiency. Ingest IQ and Event IQ help drive enhanced conversions and optimize marketing campaigns through precision tracking and real-time behavioral insights.
6. Orchestrate Data Across Channels
Coordinating messages and campaigns across platforms ensures consistent user experiences without overexposing sensitive information. For example, aligning email, app, and website data avoids conflicting messaging or duplicate data collection. Event IQ enables cross-channel marketing orchestration, providing actionable insights while keeping all customer data secure and compliant.
7. Analyze and Act on Insights Responsibly
Using analytics responsibly allows you to measure campaign performance and personalize experiences while minimizing PII exposure. For instance, segmenting audiences based on first-party data improves targeting without relying on risky third-party identifiers. Ingest IQ and Ingest ID deliver analytics, insights, and CDP capabilities, empowering you to make data-driven decisions safely.
As you begin to implement these safeguards, it’s important to understand how various privacy laws come into play, especially when handling customer data.
Data Privacy Laws and PII
Understanding data privacy laws is crucial when you handle large volumes of customer data across multiple platforms and campaigns. These regulations define how you must collect, store, and process PII while protecting your business from penalties. Here are the key privacy laws relevant to your operations:
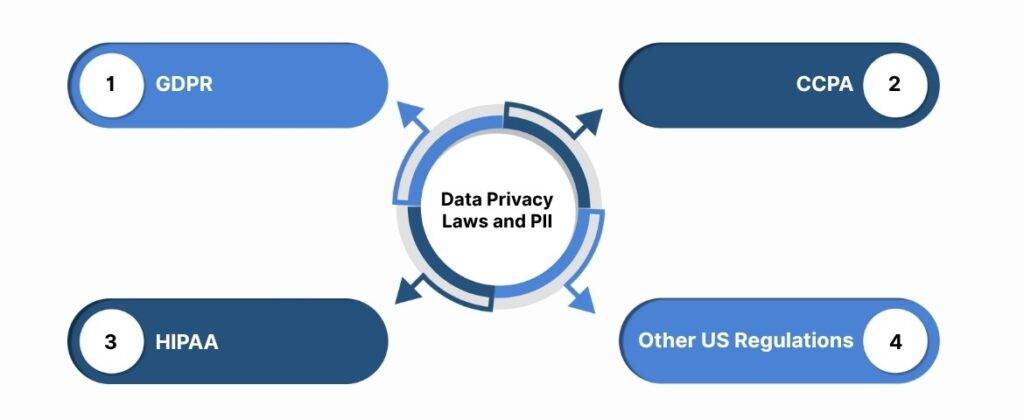
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): Applies primarily in Europe but impacts any business handling EU residents’ data. Requires consent for data collection, rights to access and delete personal data, and accountability in processing. For example, you must obtain explicit consent before tracking user behavior across e-commerce and marketing platforms.
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act): Grants California residents rights to know, delete, or opt out of the sale of their personal information. Businesses must provide clear notice of data collection and respond to consumer requests within specified timelines. For instance, your marketing campaigns must respect opt-out preferences to avoid fines.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): Protects sensitive health information, particularly relevant if your campaigns involve health or wellness data. Requires secure storage, controlled access, and breach notification procedures. For example, if you run wellness campaigns, any collected health data must be encrypted and access-restricted.
- Other US Regulations: Depending on the state or industry, laws like GLBA (financial data), COPPA (children’s data), or state-specific privacy acts may apply. For example, collecting PII from minors or financial data requires additional safeguards and parental consent.
Event IQ helps maintain privacy compliance by managing consent and enforcing regulatory rules across all digital marketing channels and campaigns.
With privacy laws in mind, let’s now look at the practical steps businesses can take to protect PII from breaches and misuse.
Also read: The Privacy Revolution in Marketing: A Guide to Navigating the New Landscape
Protecting PII
Protecting PII is essential to maintain customer trust, comply with regulations, and safeguard your marketing performance. Here are key strategies you should implement:
- Encrypt Sensitive Data: Protect customer information both in transit and at rest.
- Limit Access: Only allow authorized team members to handle PII.
- Use Strong Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication for all data platforms.
- Regular Audits: Review data practices and access logs to spot vulnerabilities.
- Educate Your Team: Train employees on privacy best practices and phishing prevention.
- Monitor for Breaches: Continuously track unusual activity and respond immediately.
Ingest IQ’s server-side tracking and real-time monitoring ensures PII is collected and managed securely across all digital channels.
Final Thoughts
Understanding PII’s meaning isn’t optional; it’s essential for compliance, customer trust, and sustainable business growth. By protecting personal data and applying strong privacy practices, you reduce risks and strengthen your reputation. Understanding what qualifies as PII, how it can be exposed, and the strategies to safeguard it empowers your business to operate confidently and responsibly. Implementing advanced data practices reduces risk while optimizing the effectiveness of your data-driven initiatives.
Ingest Labs offers powerful solutions to help you manage and protect customer data across channels. With Ingest IQ for server-side tracking and analytics, Ingest ID for unified customer profiles, and Event IQ for cross-channel insights, you can ensure privacy compliance, optimize conversions, and orchestrate campaigns effectively. These tools enable you to turn data into actionable insights while safeguarding PII throughout the customer journey.
Reach out to Ingest Labs today to safeguard your customer data and optimize your marketing campaigns with privacy-first solutions.
FAQ
1. What is PII, and why is it important for businesses?
PII (Personally Identifiable Information) includes data that can identify an individual, and protecting it is critical for compliance, customer trust, and secure marketing campaigns.
2. How can businesses prevent PII theft in digital marketing and e-commerce?
Companies can prevent PII theft through server-side tracking, encryption, restricted access, employee training, and real-time monitoring of data flows.
3. What are the main differences between sensitive and non-sensitive PII?
Sensitive PII, such as Social Security numbers or financial data, can lead to identity theft, while non-sensitive PII, like names or ZIP codes, requires careful handling but poses a lower immediate risk.
4. Which privacy laws should US-based companies follow to protect PII?
Businesses in the US must comply with CCPA, HIPAA, and other state or federal privacy regulations to secure customer information and avoid penalties.
5. What are common methods hackers use to steal PII?
Common methods include phishing emails, malware attacks, social engineering, insider threats, and exploiting weak authentication or unsecured systems.