Most businesses believe they understand their customers. In reality, many are making decisions based on incomplete, fragmented, or outdated information. In 2025, 52% of US marketers say first-party data is now their primary source of insight, a clear signal that customer data has shifted from a supporting role to a core business asset. When customer data is misunderstood or poorly collected, it does not just affect reporting. It directly impacts targeting, personalization, attribution, and revenue growth.
For digital marketers, e-commerce teams, and agencies operating in a privacy-regulated environment, knowing what customer data you collect and how you collect it matters more than ever. This guide breaks down the key types of customer data, the most effective collection methods, and how businesses can use customer data responsibly to drive measurable outcomes while staying compliant with modern data protection laws.
Key Takeaways
- Understand customer data: Learn the types of data businesses collect, from demographics to engagement and first-party identity, and why each matters.
- Collect data effectively: Explore methods like digital tracking, CRM systems, surveys, social listening, loyalty programs, and offline capture for actionable insights.
- Ensure quality and compliance: High-quality, accurate data combined with privacy-focused practices ensures trust, ethical management, and adherence to GDPR/CCPA.
- Drive business outcomes: Use customer data for segmentation, personalization, attribution, predictive modeling, and ROI measurement to optimize campaigns and growth.
What Is Customer Data?
Customer data is information that helps businesses understand who their customers are, how they behave, and what they value. It includes details about demographics, purchase history, interactions, preferences, and engagement patterns. By collecting and analyzing this data, marketers can make informed decisions, tailor personalized experiences, and identify opportunities to optimize campaigns and drive growth.
For businesses, customer data is not just a reporting tool. It underpins marketing strategies, enabling precise segmentation, targeted messaging, and competitive differentiation. Companies that leverage accurate, actionable customer data can improve conversion rates, enhance customer retention, and create a sustainable advantage in today’s data-driven marketplace.
Why Customer Data Matters for Businesses
Accurate and well-managed customer data drives measurable business outcomes. For marketers, e-commerce teams, and agencies, it provides clarity, precision, and actionable insights that improve overall performance. Here are the key benefits of using customer data effectively:
- Precise Targeting: Helps identify the right audience segments and deliver messages to those most likely to engage.
- Improved Conversion Rates: Enables optimization of campaigns based on behavioral and transactional insights.
- Personalization at Scale: Supports tailored offers and content, increasing engagement, repeat purchases, and customer lifetime value.
- Enhanced Retention and Loyalty: Tracks customer interactions to proactively prevent churn and strengthen long-term relationships.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Provides reliable insights for allocating budgets, optimizing pricing, and improving operational efficiency.
- Compliance and Trust: Ensures adherence to privacy laws such as CCPA and GDPR, building customer confidence and reducing legal risk.
- Attribution and Performance Measurement: Facilitates accurate campaign measurement and ROI analysis for better marketing accountability.
- Strategic Advantage: Helps businesses recognize trends, patterns, and opportunities faster than competitors relying on incomplete data.
- Cross-Channel Consistency: Ensures messaging and campaigns are aligned across web, email, mobile, and other channels.
- Innovation and Experimentation: Provides insights to test new strategies, products, and marketing approaches with reduced risk.
By understanding these benefits, businesses can make informed decisions, optimize campaigns, and create meaningful experiences for their customers.
Key Types of Customer Data
To make informed marketing decisions, businesses must understand the different types of customer data. Each type provides unique insights that help optimize campaigns, personalize experiences, and measure performance effectively.
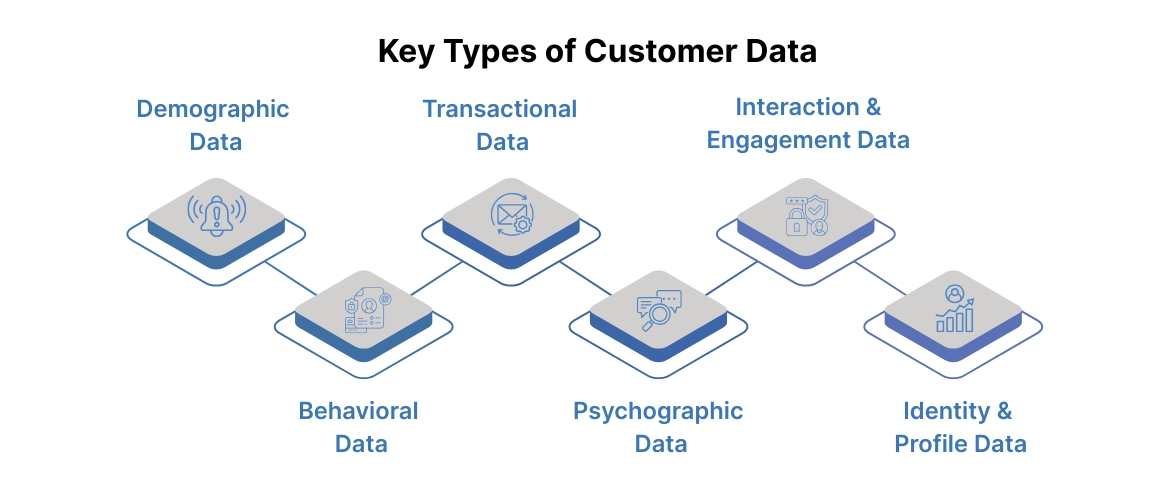
1. Demographic Data
Demographic data tells you who your customers are, making it easier to target and segment them effectively.
- Age
- Gender
- Income
- Education level
- Location
- Household size
- Occupation
Business Value: Enables precise segmentation for campaigns, product positioning, and targeted offers. Helps identify which audience groups are most profitable or receptive to specific messaging.
2. Behavioral Data
Behavioral data shows what your customers do and how they interact with your brand across digital channels.
- Website visits and page views
- Clickstream and navigation patterns
- App usage and feature interactions
- Frequency and timing of engagement
- Search and content consumption behavior
Business Value: Allows prediction of customer intent, personalization of user journeys, and optimization of marketing funnels to increase conversions.
Also read: Defining Behavioral Segmentation in Marketing with 10 Examples and Strategies - Ingest Labs
3. Transactional Data
Transactional data captures what customers buy and how they engage in purchasing.
- Purchase history and order frequency
- Average order value
- Product preferences
- Payment methods used
- Returns and refunds
Business Value: Critical for revenue analysis, campaign ROI measurement, and customer lifetime value calculation. Supports pricing, bundling, and promotional strategies.
4. Psychographic Data
Psychographic data explains why customers behave the way they do by revealing their values, attitudes, and interests.
- Interests and hobbies
- Lifestyle choices
- Values and beliefs
- Personality traits
- Opinions and attitudes
Business Value: Enhances messaging relevance, guides content strategy, and helps build emotional connections with customers.
5. Interaction & Engagement Data
Interaction and engagement data measures how customers interact with your campaigns, content, and channels.
- Email open and click rates
- Social media engagement
- Ad interactions
- Time spent on website pages
- Content downloads and shares
Business Value: Helps optimize creative strategies, channels, and messaging based on real engagement patterns. Enables A/B testing and performance tracking.
6. Identity & Profile Data
Identity and profile data ties all customer information together, creating unified profiles for personalization and accurate attribution.
- Email addresses and login credentials
- First-party identifiers
- Customer ID numbers
- Cross-device and cross-channel identity mapping
- Profile enrichment from interactions
Business Value: With tools like Ingest Labs’ Ingest ID, businesses can assign a persistent first-party identifier to each unique visitor. This allows marketers to unify interactions across platforms, personalize experiences, accurately attribute conversions, and maintain compliance with privacy regulations. First-party identity data forms the foundation for privacy-first, data-driven marketing in a cookieless world.
Also read: Understanding the Importance and Benefits of Using First-Party Data in Marketing - Ingest Labs
Customer Data Sources and Formats
Understanding the origin and type of customer data is crucial for making informed marketing, analytics, and personalization decisions. Customer data can differ in source and format, and each category has specific applications and business value.
Primary vs Secondary Data
| Type | Description | Examples |
| Primary Data | Data collected directly by the business from its own customers. | Surveys, feedback forms, transactional records, website/app analytics, email/chat interactions |
| Secondary Data | Data sourced from third parties or external sources. | Market research reports, industry studies, syndicated datasets, social media monitoring |
Quantitative vs Qualitative Data
| Type | Description | Examples |
| Quantitative Data | Numerical and measurable data used for analysis and decision-making. | Sales figures, order frequency, website traffic, click-through and conversion rates |
| Qualitative Data | Descriptive data capturing opinions, motivations, and sentiments. | Customer feedback, open-ended survey responses, social media comments, focus groups |
By combining both sources and formats, businesses gain a holistic view of their customers. Primary and quantitative data offer precision and measurement, while secondary and qualitative data provide context and trend awareness. Together, they enable data-driven strategy, personalized marketing, and compliance-ready insights.
How to Collect Customer Data Effectively
Collecting customer data effectively is critical for marketers, e-commerce teams, and agencies. Understanding the right methods ensures accurate, actionable insights while maintaining customer trust and compliance with privacy regulations. Using structured approaches to collect data helps businesses make better decisions, optimize campaigns, and deliver personalized experiences.
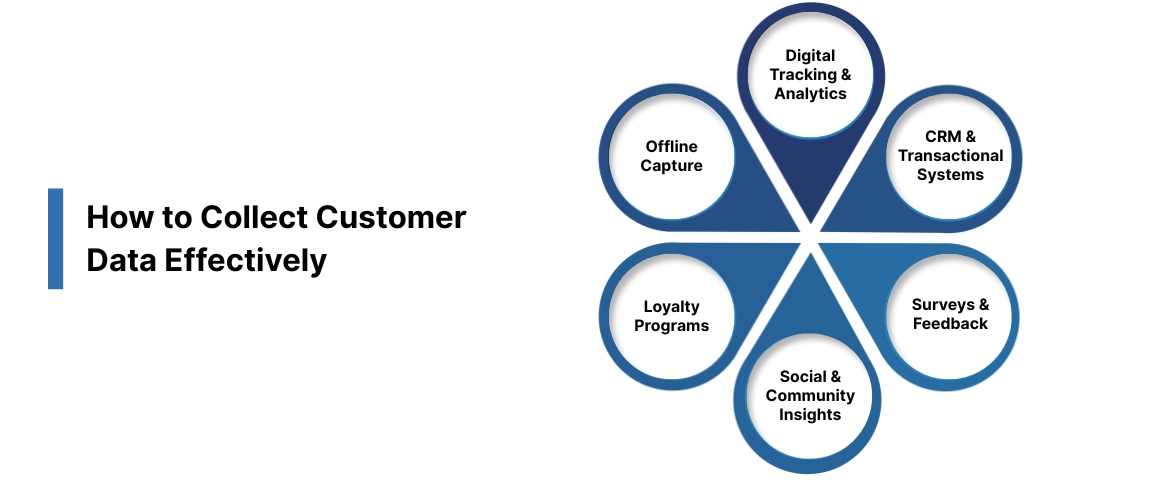
1. Digital Tracking & Analytics
Digital tracking captures customer interactions across websites, mobile apps, and other digital channels, helping businesses analyze behavior, optimize marketing funnels, and improve personalization. It provides a real-time foundation for decision-making and performance measurement.
Best Use Cases
- Tracking website visits, page views, and session duration
- Monitoring clicks, conversions, and form submissions
- Optimizing content strategy and digital marketing funnels
How to Apply
- Use first-party tracking methods like Ingest IQ for server-side collection
- Obtain explicit customer consent and provide clear privacy notices
- Monitor and validate tracking regularly to ensure accuracy
| Pros | Cons |
| Real-time data capture for faster decisions | Dependent on user consent for privacy compliance |
| High scalability and automation | Limited if users block cookies or tracking |
| Supports cross-channel attribution | Requires technical setup and monitoring |
Also read: Understanding How server side Tracking Works - Ingest Labs
2. CRM & Transactional Systems
CRM and transactional systems collect structured customer data from purchases, subscriptions, and stored profiles, giving a verified view of customer activity and supporting personalized campaigns.
Best Use Cases
- Tracking purchase history, subscriptions, and recurring orders
- Segmenting customers for targeted email or loyalty campaigns
- Centralizing customer profiles for cross-channel insights
How to Apply
- Integrate CRM with marketing automation platforms
- Maintain encrypted storage and limit access to authorized personnel
- Regularly clean and update data to avoid duplicates and errors
| Pros | Cons |
| Highly accurate and verified data | Can become siloed if not integrated across platforms |
| Easy integration with automation tools | Requires ongoing maintenance |
| Supports revenue analysis and ROI measurement | Risk of outdated or duplicate entries |
3. Surveys & Feedback
Surveys and feedback collect direct insights from customers regarding preferences, satisfaction, and experiences. This qualitative approach helps identify pain points, inform improvements, and refine campaigns.
Best Use Cases
- Gathering product or service feedback
- Measuring customer satisfaction (e.g., NPS)
- Collecting insights on campaigns or website experience
How to Apply
- Keep surveys short, focused, and easy to complete
- Communicate clearly why data is collected and how it will be used
- Anonymize responses where appropriate to protect privacy
| Pros | Cons |
| Captures qualitative insights | Response rates may be low |
| Direct feedback from customers | May require incentives |
| Supports innovation and experience optimization | Subject to bias in answers |
4. Social & Community Insights
Social listening and community monitoring gather publicly available customer opinions on social platforms, forums, and review sites. This helps brands understand sentiment, identify trends, and engage proactively.
Best Use Cases
- Monitoring brand perception and customer sentiment
- Identifying market trends and unmet needs
- Tracking competitor activity and customer discussions
How to Apply
- Use AI-powered social listening tools for large-scale monitoring
- Respect privacy by only analyzing public posts
- Respond strategically to customer feedback and queries
| Pros | Cons |
| Real-time insights into customer sentiment | Data can be unstructured and noisy |
| Captures broader market trends | Requires AI or specialized tools for analysis |
| Enhances engagement opportunities | Potential privacy concerns if misused |
5. Loyalty Programs
Loyalty programs incentivize customers to opt-in for data collection, giving brands access to high-quality, permission-based datasets while driving engagement.
Best Use Cases
- Collecting emails, contact info, and purchase preferences
- Encouraging repeat purchases and increasing retention
- Building richer first-party datasets
How to Apply
- Clearly communicate data collection purposes to participants
- Offer opt-out options for transparency
- Limit data collected to what is necessary for rewards
| Pros | Cons |
| High-quality, opted-in customer data | May attract only highly engaged users |
| Strengthens customer relationships | Requires management of rewards and incentives |
| Supports personalized marketing | Limited data diversity |
6. Offline Capture
Offline capture gathers customer data in-person, such as at events, retail locations, or through interviews, complementing digital data collection.
Best Use Cases
- Collecting customer info at retail locations or events
- Conducting in-depth interviews for product or service feedback
- Capturing offline purchase details or preferences
How to Apply
- Obtain explicit consent from participants
- Digitize offline data promptly and securely
- Align with privacy policies and regulations
| Pros | Cons |
| Captures data unavailable online | Manual collection is time-consuming |
| Provides rich qualitative insights | Data integration with digital systems can be challenging |
| Builds personal relationships | Risk of human error |
By applying these methods thoughtfully, businesses can collect high-quality customer data that drives actionable insights, enables personalization, and ensures compliance with privacy regulations, forming the foundation for data-driven marketing success.
Data Quality, Privacy & Compliance for Customer Data
High-quality customer data is only valuable if it is accurate, reliable, and collected responsibly. Businesses that prioritize privacy and compliance not only avoid legal risks but also build trust and unlock new marketing opportunities. In North America, regulations like GDPR and CCPA make ethical data collection and management critical for success.
GDPR & CCPA Compliance for Customer Data
Understanding data privacy laws is essential for businesses operating in the US and Canada. These regulations require companies to protect personal data, respect customer consent, and ensure transparency in collection and usage. Compliance is both a legal necessity and a competitive advantage.
Tips for Compliance:
- Managing customer consent across websites, apps, and offline channels
- Ensuring opt-in and opt-out mechanisms for marketing communications
- Conducting regular audits of stored customer data
Also read: Ultimate Guide to GDPR Compliance in Shopify - Ingest Labs
Ethical Management of Customer Data
Ethical handling of customer data ensures that businesses respect privacy, maintain transparency, and store data securely. Beyond compliance, ethical practices increase customer confidence and engagement.
Tips for Ethical Data Use:
- Collecting only necessary data for specific business objectives
- Clearly communicating how customer data will be used
- Regularly reviewing and deleting outdated or irrelevant data
By prioritizing data quality, privacy, and compliance, businesses can harness customer data responsibly, unlock actionable insights, and create trust-based relationships while staying fully aligned with North America regulations.
How to Use Customer Data to Drive Business Outcomes
Collecting customer data is only the first step; its true value lies in turning insights into actionable strategies. Businesses that leverage data effectively can personalize experiences, optimize campaigns, and predict trends, giving them a competitive advantage in North America’s data-driven market.
1. Segmentation & Personalization
Segmentation divides customers into meaningful groups based on demographics, behavior, purchase history, and preferences. Personalization delivers targeted messages, offers, and experiences for each segment.
Actionable Ways to Apply:
- Group customers by purchase frequency, order value, and product preferences
- Personalize emails, push notifications, and website content for each segment
- Use behavior-triggered campaigns, such as abandoned cart reminders
- Tailor offers based on lifecycle stage, e.g., new vs. loyal customers
- Test personalized campaigns to optimize engagement and conversions
Business Impact: Increases engagement, conversion rates, and repeat purchases while strengthening brand loyalty.
2. Attribution & ROI Measurement
Attribution connects customer actions to specific marketing campaigns and channels, allowing businesses to measure ROI accurately. This ensures resources are spent where they drive the most value.
Actionable Ways to Apply:
- Track multi-channel interactions to understand the full customer journey
- Attribute conversions to touchpoints like email, paid ads, and social campaigns
- Analyze ROI by campaign, product line, or audience segment
- Identify underperforming channels to reallocate budgets efficiently
- Use data-driven dashboards for real-time performance monitoring
Business Impact: Enables better budget allocation, improved campaign effectiveness, and measurable growth in marketing ROI.
3. Predictive Modeling
Predictive modeling uses historical and behavioral data to anticipate future customer actions, such as churn, purchases, or engagement. This proactive approach helps businesses act before potential issues impact revenue.
Actionable Ways to Apply:
- Identify customers at risk of churn and implement retention campaigns
- Forecast demand for products or services to optimize inventory
- Predict customer lifetime value to prioritize high-value segments
- Personalize recommendations based on predicted preferences
- Optimize campaign timing and messaging for maximum effectiveness
Business Impact: Reduces churn, improves retention, maximizes revenue opportunities, and increases efficiency in marketing campaigns.
Conclusion
Customer data is the backbone of modern marketing and business growth. Collecting it responsibly, ensuring quality, and using it strategically allows businesses to deliver personalized experiences, optimize campaigns, and make data-driven decisions. From segmentation and predictive modeling to accurate attribution and privacy compliance, the right approach transforms raw data into a competitive advantage. Companies that master customer data are better positioned to engage their audience, increase loyalty, and maximize ROI.
Ingest Labs provides a suite of privacy-first tools that make collecting, unifying, and analyzing customer data actionable and reliable:
- Ingest ID: Creates unique first-party identifiers to unify customer profiles for precise tracking and personalization.
- Ingest IQ: Enables server-side tracking for accurate, privacy-compliant data collection across websites and apps.
- Event IQ: Aggregates and analyzes customer interactions from multiple sources to deliver actionable insights, optimize campaigns, and improve retention.
Ready to turn your customer data into measurable business outcomes? Book a demo with Ingest Labs today and see how our tools can drive growth for your business.
FAQs
1. What is customer data and why is it important for business growth?
Customer data is information about customers’ demographics, behavior, purchases, preferences, and engagement. It helps businesses personalize marketing, improve experiences, and make data-driven decisions to drive growth.
2. What types of customer data should businesses collect?
Collect demographic, behavioral, transactional, psychographic, and engagement data. Together, these create a holistic view to tailor strategies and optimize marketing efforts.
3. How can customer data be collected responsibly and ethically?
Collect data with explicit consent, transparent privacy notices, and secure storage. Only gather necessary information while complying with GDPR and CCPA to maintain trust.
4. How does first‑party customer data differ from third‑party data?
First-party data is collected directly from customers, making it accurate and privacy-friendly. Third-party data is sourced externally and often less reliable due to privacy restrictions.
5. How can businesses use customer data to improve marketing ROI?
Use customer data to segment audiences, personalize campaigns, attribute conversions, predict behavior, and optimize marketing spend for measurable results.