Every user interacts with your brand through a series of steps: discovering, exploring, deciding, and returning. Each of these moments contributes to the overall experience and determines how effectively your marketing and product strategies perform.
User journey mapping helps your team understand those steps with clarity. It visualizes every stage of interaction, from the first impression to conversion, and reveals how people experience your brand. This process replaces assumptions with data, allowing you to see what drives engagement and what needs improvement.
In a privacy-focused digital environment, accurate journey mapping relies on reliable, first-party data when supported by tools you can track, visualize, and refine every stage of the user journey with confidence.
Now that we understand its purpose, let’s define what journey mapping means and why it has become a key part of modern marketing and analytics.
Key Takeaways
- Journey mapping shows how users interact with your brand and where improvements create measurable impact.
- Using data-driven insights turns a simple diagram into a real optimization framework for conversions and retention.
- Privacy-first tools like Ingest IQ, Event IQ, and Ingest ID make journey mapping accurate, compliant, and reliable.
- A well-built journey map helps your team act faster, reduce guesswork, and deliver experiences users truly value.
What Is User Journey Mapping?
User journey mapping is the process of documenting how individuals move through your digital experience, from discovery to decision. It identifies the actions, motivations, and obstacles users face at each stage and connects them to measurable outcomes such as conversions or retention.
Rather than relying on opinion or observation, modern journey mapping uses data from real user behavior. This includes signals captured through analytics tools, tracking systems, and first-party data sources.
Platforms such as Ingest Labs’ Event IQ and Ingest IQ simplify this process, collecting data accurately across channels without relying on third-party cookies.
A well-designed journey map transforms fragmented insights into a clear picture of how people interact with your business, helping teams make practical, informed decisions that improve performance.
Purpose and Importance of Journey Mapping
Journey mapping provides a unified view of how users experience your brand. It aligns marketing, analytics, and product teams around shared data and shared goals.
Why it matters:
- It identifies points of friction that cause users to abandon or disengage
- It reveals opportunities for better personalization and conversion optimization.
- It helps teams measure how effectively campaigns and experiences meet user needs.
By connecting behavioral data with emotional context, your team gains insight into what motivates or discourages users. When supported by accurate tracking and privacy-compliant data, journey mapping becomes a tool for strategic growth, one that replaces guesswork with measurable understanding.
With this foundation in place, we can now look at the core components that make an effective user journey map and how each element contributes to better marketing outcomes.
Also Read: Track the Customer Journey Across Multiple Channels with Ingest Labs
Core Components of a User Journey Map
A strong user journey map is built on a clear structure. Each component represents an essential piece of how users interact with your business. When combined, these elements reveal not only what users do, but why they do it.
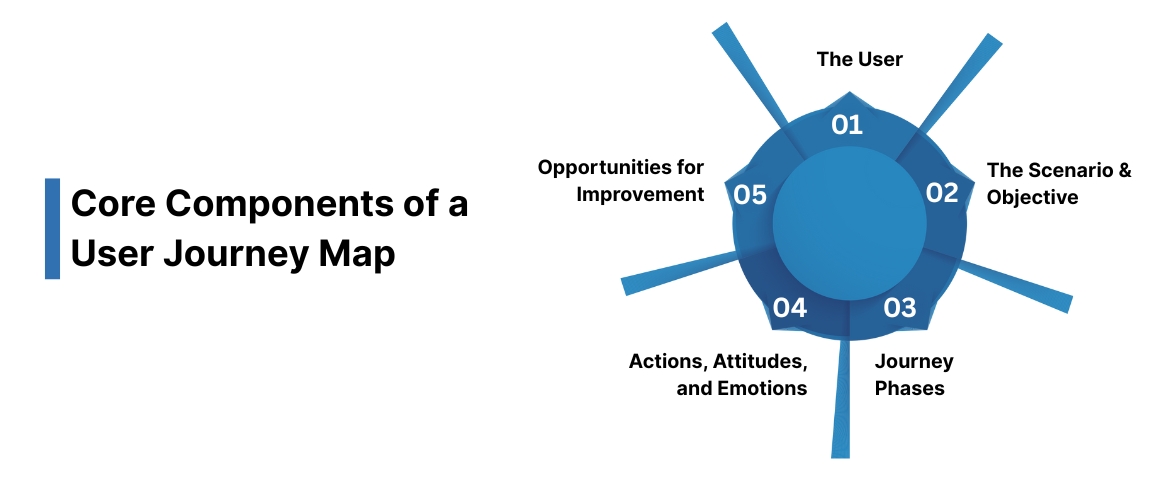
1. The User: Personas and Archetypes
Every journey begins with the user. A clear persona defines who you are designing for — their goals, motivations, and challenges. Marketers often base these profiles on analytics data and customer interviews.
With platforms like Ingest ID, teams can create unified, first-party profiles that combine behavioral and demographic data, giving a complete understanding of each audience segment.
2. The Scenario and Objective
Each journey map should focus on a specific goal or task. This could be completing a purchase, booking a demo, or renewing a subscription.
Defining the objective helps your team concentrate on the steps that matter most to conversion and satisfaction.
3. Journey Phases: Awareness, Engagement, Decision, Retention
Mapping the journey through key phases allows you to understand where users first interact, what influences their decision-making, and what keeps them returning. Each phase should include both measurable actions and user sentiment.
4. Actions, Attitudes, and Emotions
Effective journey maps connect behavior with motivation. Quantitative data, such as clicks and form submissions, reveal what users do, while qualitative insights explain why they behave that way. This combination helps identify areas where expectations and experiences differ.
5. Opportunities for Improvement
Every journey map should highlight gaps that limit conversions or satisfaction. These may include unclear messaging, long forms, or missing follow-ups. By analyzing tracked data through platforms such as Event IQ, marketers can prioritize improvements that have a measurable impact.
When these components work together, the journey map becomes a dynamic framework for continuous optimization rather than a one-time exercise.
Example:
An eCommerce marketer analyzing checkout behavior might find users drop off during payment. Combining behavioral data from Event IQ and profile insights from Ingest ID reveals that long form fields cause frustration, turning a vague problem into an actionable fix.
Tip: Treat your journey map as a living framework. Update it regularly with new analytics and conversion data to keep it accurate and relevant.
Also Read: Building a Unified Customer Profile: Understanding Your User
User Journey Map vs. Customer Journey Map
Many professionals use “user journey” and “customer journey” interchangeably. While both are related, they serve distinct business purposes. Understanding the difference ensures your team focuses on the right insights.
| Aspect | User Journey Map | Customer Journey Map |
| Focus | Specific interactions within a product, website, or app. | Broader relationship across marketing, sales, and service touchpoints. |
| Goal | Improve usability and experience. | Strengthen retention and brand engagement. |
| Data Source | Behavioral and event tracking (e.g., Ingest IQ, Event IQ). | CRM, support, and post-purchase feedback. |
| Primary Use Case | Conversion optimization and UX improvements. | Lifecycle management and customer loyalty strategy. |
Example:
- A user journey map helps identify why users abandon the checkout process.
- A customer journey map tracks how customers interact after purchase, such as email campaigns or support requests.
Both maps work best together. A user journey map fixes friction inside the product; a customer journey map ensures engagement continues beyond it.
How Ingest Labs Bridges the Two:
With Ingest IQ, businesses can capture cross-channel events (ads, emails, web interactions) and link them with first-party user data from Ingest ID.
This integration helps teams view both micro and macro journeys in one place, building a complete understanding of customer experience.
Also Read: How to Perform User Behavior Tracking and Analysis
Types of User Journey Maps
User journey maps can serve different purposes depending on where your organization is in its data or optimization process. Understanding each type helps you choose the right approach for your goals.
1. Current-State Journey Map
A current-state map visualizes how users interact with your brand right now. It is built from existing behavioral data, analytics reports, and qualitative insights.
What it does:
- Highlights real user behavior across channels.
- Identifies friction points, gaps, and inefficiencies.
- Serves as a diagnostic tool for current performance.
Use Case Example:
A marketing team uses Event IQ to track engagement from ad clicks to checkout. The map shows users dropping off after viewing shipping costs, revealing a key optimization opportunity.
2. Future-State Journey Map
A future-state map represents your ideal customer experience based on strategic goals. It outlines what you want users to do, feel, and experience after improvements are implemented.
Why it matters:
- Helps align teams on a shared vision of the desired journey.
- Encourages data-backed decision-making to close experience gaps.
- Provides a roadmap for UX, content, and marketing optimization.
Use Case Example: Using Ingest IQ and Ingest ID, a business models how a future checkout experience could reduce abandonment by simplifying forms and improving personalization.
3. Day-in-the-Life Journey Map (Advanced)
This map goes beyond direct brand interactions and explores how users behave in daily contexts. It helps marketers understand where their product or service fits into the user’s broader life or work routine.
Ideal for:
- B2B brands are analyzing user workflow integration.
- Consumer brands studying lifestyle or time-based behavior.
- Teams are planning cross-channel engagement strategies.
Tip: Start with a current-state map to identify what’s broken, then create a future-state map to plan how to fix it.
Also Read: Types and Use of Click Attribution Models
Process of Creating a User Journey Map
Creating a user journey map combines data analysis, creative thinking, and collaboration. The goal is to turn complex interactions into clear, actionable insights.
Follow this structured process to ensure accuracy and usability:
Step 1: Define User Personas and Goals
Begin by outlining your main audience segments and what they want to achieve. Use analytics and CRM data to validate assumptions.
- Identify motivations and pain points.
- Link goals to measurable outcomes, such as sign-ups or purchases.
- Ingest ID helps refine personas through unified, first-party data profiles.
Step 2: Identify Customer Touchpoints
List every place where users interact with your brand, across channels, devices, and campaigns.
- Include ads, social media, website visits, emails, and product usage.
- Understand what triggers each interaction and how users respond.
- Ingest IQ enables unified data collection across all these touchpoints for complete visibility.
Step 3: Visualize Journey Phases
Organize user interactions into clear stages, such as:
- Awareness
- Consideration
- Decision
- Retention
Map actions, emotions, and expectations within each stage. This helps you see where users advance smoothly or encounter barriers.
Step 4: Capture User Actions and Responses
Use behavioral tracking tools to measure how users engage. Combine quantitative and qualitative insights to build a complete story.
- Track actions like page visits, clicks, and form completions.
- Collect feedback and sentiment to understand motivations.
- Event IQ captures these actions in real time while maintaining privacy compliance.
Step 5: Validate and Iterate the Map
Once the map is built, test its accuracy against live data. Update it regularly as campaigns and behaviors evolve.
- Review analytics and user feedback periodically.
- Identify any new friction points that appear after changes.
- Adjust your strategies based on updated insights.
Pro Tip: Treat your journey map as an evolving tool. As user behavior and privacy standards change, update your map with first-party data and server-side tracking to maintain accuracy.
Also Read: Understanding and Implementing Campaign Optimization
Data-Driven Journey Mapping: The Analytics Advantage
Traditional journey mapping often relies on interviews, surveys, and observation. While these methods provide valuable context, they miss a crucial dimension: data accuracy.
A data-driven approach transforms journey mapping from a one-time workshop exercise into a continuous optimization process powered by real-time analytics.
Why Data-Driven Journey Mapping Matters
When you base your maps on actual user behavior, every decision is backed by measurable evidence. This approach helps your team:
- Identify drop-off points using quantitative data from event tracking.
- Discover hidden pathways that lead to conversions or churn.
- Correlate actions with outcomes, revealing which steps directly influence ROI.
- Validate assumptions about audience intent, engagement, and satisfaction.
The Role of Data and Analytics
Accurate journey mapping depends on capturing complete, privacy-compliant user signals. Here’s how analytics tools enhance every stage of mapping:
| Mapping Stage | Data Role | Outcome |
| Defining Personas | Use first-party data to validate demographics and behavior. | Realistic, data-backed personas. |
| Identifying Touchpoints | Track all digital interactions across web, app, and campaigns. | Comprehensive visibility. |
| Measuring Emotions and Actions | Combine qualitative feedback with event data. | Balanced insights into user motivation. |
| Validating the Map | Test journey assumptions against live data. | Reliable, updated journey visualization. |
How Ingest Labs Powers Data-Driven Mapping
Ingest Labs enables marketers to build data-driven journey maps with unmatched accuracy and compliance.
- Event IQ provides real-time tracking of every user action across websites and applications.
- Ingest IQ delivers server-side data collection for complete visibility without relying on cookies.
- Ingest ID connects actions to unified user profiles, helping marketers identify recurring behaviors and preferences.
Together, these tools replace guesswork with precision, turning customer journeys into measurable performance systems.
Practical Examples of User Journey Mapping
To see how journey mapping works in practice, let’s explore three common business scenarios. Each example shows how mapping, combined with accurate data, drives measurable improvement.
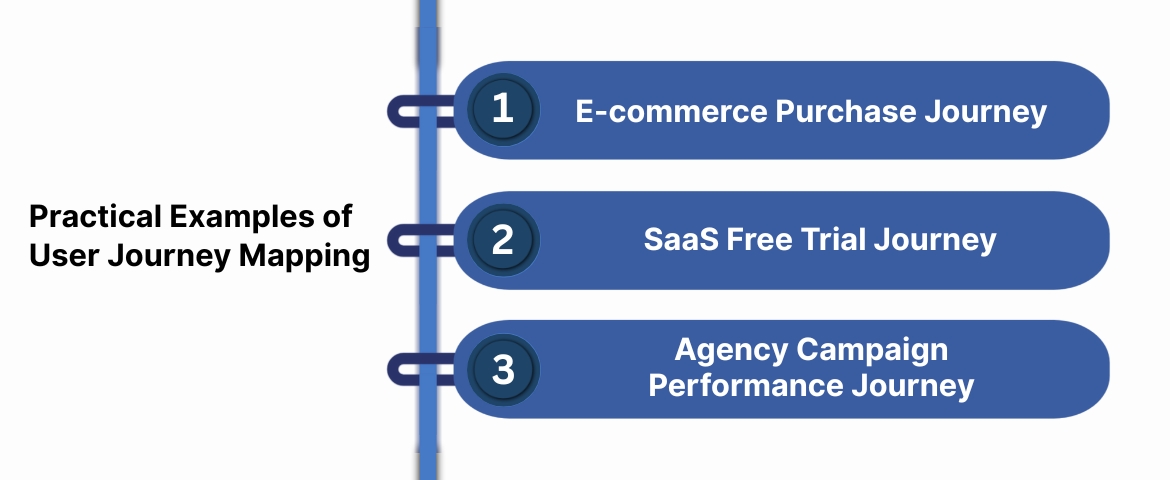
Example 1: E-commerce Purchase Journey
Goal: Reduce cart abandonment and improve checkout conversions.
Mapping Process:
- Track user flow from product discovery to checkout using Event IQ.
- Identify drop-off stages using behavioral metrics.
- Analyze sentiment through feedback surveys or post-visit polls.
Findings:
- 60% of users leave at the shipping information step.
- Friction occurs when the total cost appears late in the process.
Actions Taken:
- Display shipping details earlier.
- Simplify checkout form.
- Use Ingest IQ for server-side tracking to ensure accurate event capture.
Result: Conversion rate improved by 28% in four weeks.
Example 2: SaaS Free Trial Journey
Goal: Increase activation rate during free trials.
Mapping Process:
- Collect data on user engagement after sign-up using Ingest ID.
- Identify key actions that lead to conversions, such as feature use or onboarding completion.
- Evaluate emotional feedback through customer success notes.
Findings:
- Users who complete onboarding within two days are twice as likely to convert.
Actions Taken:
- Add progress tracking and reminder emails.
- Use Event IQ to monitor feature usage and completion rate.
Result: Activation improved by 35%, with higher retention after conversion.
Example 3: Agency Campaign Performance Journey
Goal: Optimize multi-channel ad performance and attribution.
Mapping Process:
- Map the client campaign flow from ad click to form submission.
- Use Ingest IQ to unify data from multiple ad platforms.
- Identify which touchpoints generate the most qualified leads.
Findings:
- Paid search brings high lead volume but low conversion quality.
- Organic traffic has fewer leads but higher closing rates.
Actions Taken:
- Rebalance ad spend toward organic amplification.
- Report performance insights using Event IQ dashboards.
Result: 22% increase in marketing-qualified leads across campaigns.
Key Takeaways from These Examples
- Every journey reveals unique patterns that data helps clarify.
- Accurate tracking allows teams to find and fix the exact moments that impact conversion.
- Using privacy-compliant, server-side tools ensures insight quality without compromising data integrity.
Also Read: Ethical Data Collection driving customer loyalty and boosting business outcomes
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Even experienced marketers can face challenges when building user journey maps. Many of these issues come from unclear data, limited tracking, or inconsistent collaboration across teams. Here are the most common mistakes, and how to avoid them effectively.
1. Mapping Without Real Data
The Pitfall: Creating journey maps based only on assumptions or anecdotal insights.
Why It’s a Problem: Assumptions rarely reflect actual behavior, leading to inaccurate or misleading conclusions.
How to Avoid It:
- Use behavioral tracking tools like Event IQ to base insights on real user actions.
- Combine analytics data with user feedback to balance quantitative and qualitative perspectives.
2. Ignoring Cross-Channel Interactions
The Pitfall: Analyzing each channel in isolation without connecting them into a unified journey.
Why It’s a Problem: Modern users move across multiple touchpoints before converting ignoring this flow hides key patterns.
How to Avoid It:
- Centralize data using Ingest IQ for consistent cross-channel visibility.
- Map the journey from ad click to conversion as one continuous experience.
3. Failing to Update the Journey Map
The Pitfall: Treating a journey map as a one-time document.
Why It’s a Problem: User behavior and marketing strategies evolve; outdated maps become irrelevant.
How to Avoid It:
- Schedule quarterly reviews of your map.
- Refresh data sources and revalidate assumptions regularly.
4. Overlooking Privacy and Compliance
The Pitfall: Using tracking methods that rely on cookies or violate privacy standards.
Why It’s a Problem: Non-compliance with GDPR or CCPA can lead to legal risks and data inaccuracy.
How to Avoid It:
- Use Ingest Labs’ server-side tracking for secure, privacy-first data collection.
- Implement first-party data practices to maintain compliance and trust.
5. Lack of Team Alignment
The Pitfall: Departments create their own versions of the customer journey without collaboration.
Why It’s a Problem: Disjointed insights prevent consistent decision-making and optimization.
How to Avoid It:
- Involve marketing, analytics, UX, and sales teams in mapping sessions.
- Use Event IQ dashboards to keep all stakeholders aligned on live performance data.
Tip: Treat your journey map as a dynamic performance asset. The more it evolves with your data, the more valuable it becomes.
Also Read: Different Methods of Ads Conversion Tracking for Websites
Conclusion
User journey mapping is not only about understanding how people move through your brand, but it is also about improving the experience behind every interaction.
When informed by accurate, privacy-compliant data, it becomes one of the most powerful tools for growth.
What you gain from effective journey mapping:
- A clear view of how users experience your brand from start to finish.
- Reliable, real-time insights that reveal friction points and conversion drivers.
- A data-driven foundation for personalization, optimization, and retention.
Traditional methods often fall short because they rely on assumptions. With Ingest Labs, your team can build a journey mapping process based on facts, not guesswork.
- Ingest IQ ensures all your user data is captured accurately across channels.
- Event IQ gives you the visibility to analyze user behavior in real time.
- Ingest ID connects every data point to a unified, privacy-safe profile.
Together, these tools make mapping straightforward, reliable, and actionable.
Contact Ingest Labs to see how your marketing team can create accurate, compliant, and data-powered user journeys, all without writing a single line of code.
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of user journey mapping?
Journey mapping helps businesses visualize how users interact with their brand. It uncovers the key moments that influence engagement, satisfaction, and conversion.
2. What is the difference between user journey mapping and customer journey mapping?
A user journey map focuses on product or experience interactions, while a customer journey map covers the full brand relationship, including marketing and post-purchase touchpoints.
3. How often should a user journey map be updated?
Ideally, review and update your journey map every quarter or whenever major campaigns, product changes, or new audience data are introduced.
4. Can data improve the accuracy of journey mapping?
Yes. Data-backed mapping allows you to move from assumptions to measurable insights. Platforms such as Event IQ and Ingest IQ ensure your maps reflect actual user behavior in real time.
5. How does Ingest Labs make journey mapping easier for marketing teams?
Ingest Labs provides a no-code MarTech suite designed for marketers. Its tools enable server-side tracking, real-time analytics, and unified customer data, making accurate, compliant journey mapping simple and efficient.