Server-side tracking promises more reliable measurement by processing event data on your infrastructure rather than relying on the user's browser. However, it also exposes issues when identity parameters don't conform to platform expectations, a prime example being the "server sending invalid match key parameters for pageview event" error.
Identity mismatches matter because client-side limitations still influence how identity data is collected before it reaches your server-side logic. For instance, 30–37%of internet users globally use ad blockers, which means client-side identifiers never fire, creating gaps that server-side systems must accurately fill.
Fixing invalid match-key errors is essential to ensure every pageview contributes to accurate attribution, cohesive user identities, and reliable analytics, especially in environments that prioritize privacy and first-party data strategies.
Before we dive in:
- What it is: The error indicates that server-side PageView events include malformed, missing, or unsupported identity parameters that fail platform validation.
- Why it matters: Invalid match keys lead to inaccurate attribution, fragmented user identity, and unreliable reporting.
- Common causes: Incorrect hashing, unsupported identifiers, schema drift, consent gaps, and identity fragmentation.
- Fixes: Audit event payloads, standardize hashing and normalization, enforce schemas, align identity logic, and validate consent before events are sent.
- Long-term: Use validation at ingestion and real-time monitoring to prevent recurrence.
What Are Invalid Match Key Parameters?
Invalid match key parameters occur when identity-related fields used to associate events, such as pageviews, clicks, or conversions, fail platform validation. When these parameters are missing, incorrectly formatted, or misaligned with platform requirements, events cannot be matched accurately.
In server-side tracking setups, match keys often include first-party identifiers or hashed user data. If these values fail validation, the event may be rejected or processed without identity matching, resulting in gaps in reporting.
Over time, these errors affect delivery optimization, distort attribution models, and reduce confidence in performance data. The issue is rarely visible at the event level, which makes it easy to miss until results start drifting.
Now that we've clarified what invalid match key parameters are, the next section looks at the most common examples teams encounter and why they occur.
Common Invalid Match Key Parameters in Pageview Events
Accurate event tracking depends on a small set of identity and context parameters being sent correctly with each pageview. When these parameters are missing, misconfigured, or restricted, validation errors occur, and pageview events fail to match reliably.
The most common match key parameters involved in this error include the following.
fbp (Meta Browser Identifier)
The fbp parameter is used to identify a browser instance for Meta-related attribution and event matching. It helps connect pageview activity with downstream advertising interactions.
Errors typically occur when:
- The value is generated inconsistently between client-side and server-side events
- The parameter is passed in an unsupported format
- The identifier is missing during server-side forwarding
When fbp is invalid or unavailable, pageview events may still fire but fail to associate correctly with advertising or conversion data, weakening attribution accuracy.
IP Address
IP address data provides contextual signals for geolocation, fraud detection, and attribution modeling, subject to consent and platform policies. In server-side tracking, this value is often passed explicitly rather than inferred.
Issues arise when:
- IP addresses are malformed or incomplete
- Placeholder or anonymized values are passed incorrectly
- Consent logic blocks IP transmission without adjusting event structure
Improper handling can result in rejected events or partial processing, especially when platforms expect IP-based validation signals.
User-Agent
The user-agent string describes the device, browser, and operating system generating the event. It plays a key role in session continuity, device classification, and platform-level validation.
Common problems include:
- Missing user-agent values in server-side payloads
- Inconsistent values between browser and server events
- Incorrect formatting or truncation
When user-agent data is unavailable or invalid, pageview events may fail to match with existing sessions, leading to fragmented reporting.
Each of these parameters contributes to how platforms validate, match, and attribute pageview events. When one or more are incorrect, the event may still be accepted but fail identity resolution checks, resulting in incomplete analytics and unreliable attribution.
Addressing these parameters early in your server-side implementation reduces silent failures and improves confidence in pageview data.
Understanding where these match key issues originate makes it easier to evaluate their downstream impact on marketing performance and optimization decisions, which we'll examine next.
How Invalid Match Keys Disrupt Marketing Performance
Invalid match key parameters do not remain isolated to tracking errors. They quietly affect how marketing performance is measured and optimized.
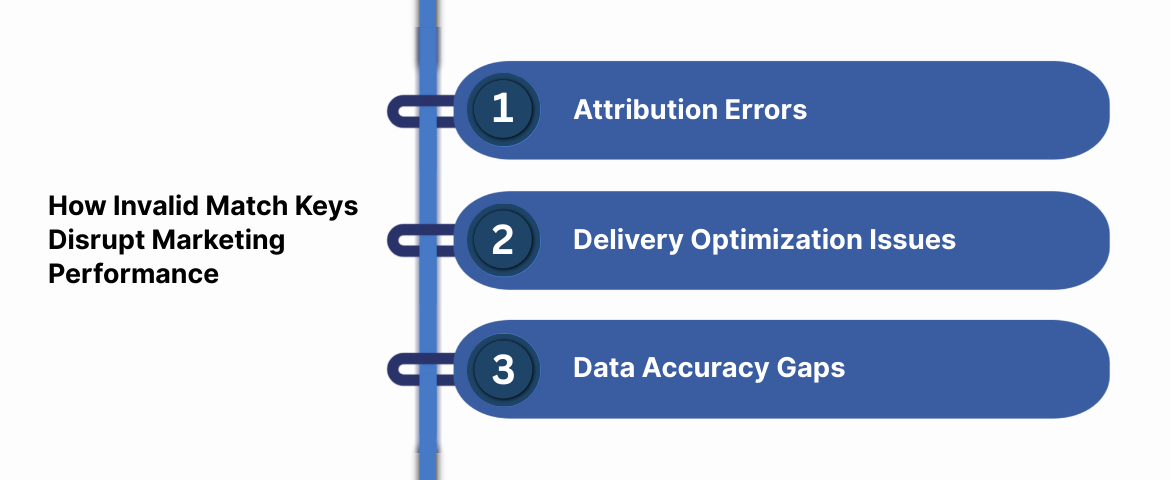
Attribution Errors
When match keys fail validation, pageview events may not link correctly to conversions. This causes attribution gaps, making it harder to understand which campaigns or channels are actually driving results. Over time, this can lead to budget shifts based on incomplete or misleading data.
Delivery Optimization Issues
Ad platforms rely on accurate event data to optimize delivery. Invalid parameters limit their ability to recognize users or learn from behavior, which can reduce campaign effectiveness. Even with steady spend, performance may decline because optimization systems lack reliable identity and event signals.
Data Accuracy Gaps
Small parameter issues can distort reporting in unexpected ways. For example, inaccurate IP or location fields can affect geographic insights and targeting decisions. When analytics no longer reflect real user behavior, confidence in reporting starts to erode.
These issues make optimization harder and introduce risk into everyday decisions. To resolve them effectively, it's important to understand what causes invalid match key parameters in server-side pageview events and how those errors are introduced.
Must read: Create a Customer Journey Map: Step-by-Step Guide for 2026
Why PageView Events Fail Due to Invalid Match Key Parameters
Server-side tracking is meant to improve data accuracy, but PageView events often surface one of the most common validation issues: invalid match key parameters. When this happens, events may fail silently, process only partially, or lose identity matching altogether, making it harder to trust campaign performance.
This issue typically appears when PageView data sent through Meta’s server-side Conversions API does not meet the platform's identity or formatting requirements. While the error message points to match keys, the root cause is usually tied to how identity data is prepared, mapped, or reused before the event is sent.
Understanding why this happens is the first step toward restoring clean, reliable tracking.
Common Causes Behind Invalid Match Key Parameter Errors
Several implementation-level issues can trigger this error. Below are the most frequent causes teams encounter during server-side PageView tracking.
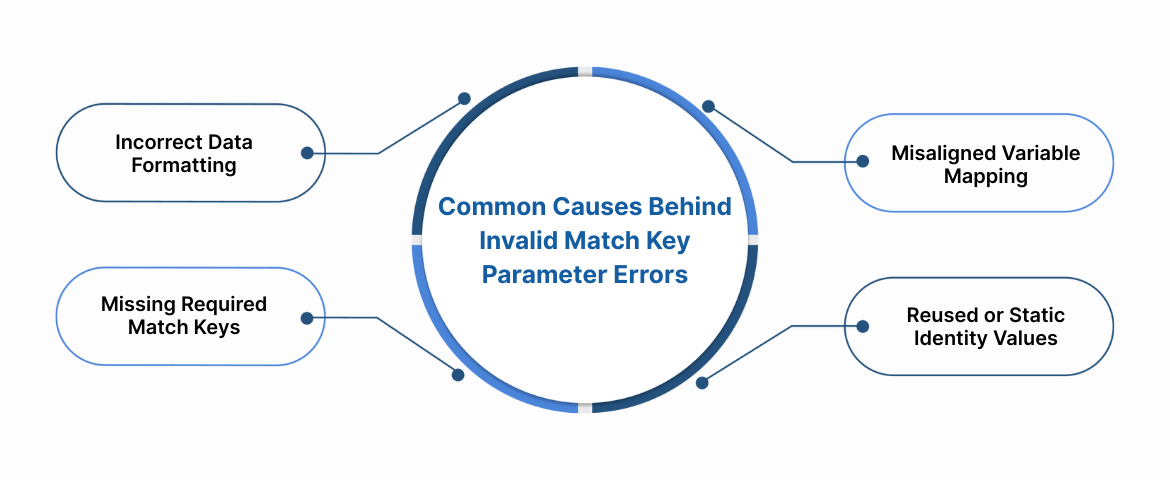
Incorrect Data Formatting
Facebook enforces strict formatting rules for match key parameters. Even minor deviations can cause validation failures.
Common examples include:
- Email addresses that do not follow standard formats (such as missing ''@'' or domain values)
- Phone numbers sent without country codes or containing non-numeric characters
- IP addresses that include invalid symbols or malformed structures
Formatting issues often occur when raw user inputs are passed directly into server-side payloads without normalization or validation.
Misaligned Variable Mapping
Another frequent issue is sending the correct data to the wrong parameter field.
This happens when:
- Phone numbers are mistakenly passed into email fields
- Auto-detected values, such as inferred location or IP-based data, are used instead of user-provided identifiers
- Fields are populated dynamically without proper checks on the value type
When match keys do not align with their expected definitions, PageView events may be rejected or stripped of identity matching.
Missing Required Match Keys
PageView events rely on identity signals to associate activity with a user or device context. If required match keys are missing, the platform cannot reliably link the event.
This commonly occurs when:
- Email, phone number, or address fields are omitted entirely
- Consent logic removes identifiers without fallback handling
- Identity data is available elsewhere, but not passed into the PageView payload
Without sufficient match keys, events lose attribution value even if they appear to fire successfully.
Reused or Static Identity Values
Using the same match key values across multiple PageView events can also trigger validation errors.
Examples include:
- Sending a single placeholder email or username for all users
- Reusing identical identifiers across sessions or devices
- Failing to refresh identity values after login or user changes
Platforms expect match keys to represent accurate, user-specific identity signals rather than static or reused values. Repeated or static values can be flagged as invalid or misleading.
Addressing these issues requires more than quick fixes. It starts with validating identity inputs, enforcing consistent formatting, and ensuring that match keys reflect real, consented user data.
In the next section, we'll look at practical steps to correct these errors and prevent them from recurring in server-side PageView tracking.
How to Resolve Invalid Match Key Errors and Keep PageView Events Clean
Invalid match key parameters usually point to inconsistencies in formatting, identity handling, or event validation within a server-side setup. Resolving the issue requires precise checks rather than broad configuration changes. The following practices help stabilize pageview tracking without adding unnecessary complexity.
Verify Match Key Formatting Early
Begin by reviewing how identity parameters are prepared before they are attached to pageview events. Even small formatting errors can cause validation failures downstream.
Key checks include:
- Email addresses: Confirm proper structure and normalization before hashing.
- Phone numbers: Include country codes and remove spaces or special characters.
- IP addresses: Ensure values contain only valid numeric characters and separators.
Preview and debug modes within your tagging setup help surface these issues before they affect live traffic.
Validate Events at the Ingestion Layer
Server-side tracking shifts responsibility for data quality upstream, making early validation critical. Pageview events should be checked before they are forwarded to analytics or advertising platforms.
Effective validation includes:
- Confirming required match keys are present
- Enforcing correct data types and formats
- Blocking unsupported or empty parameters
With Ingest IQ, validation and schema checks can be applied at the server level before events are forwarded downstream. This reduces silent failures and prevents rejected events from reaching reporting systems.
Avoid Auto-Inferred or Proxy-Based Identity Data
Auto-detected values can introduce inconsistencies, especially when used as match keys. Location or identity inferred from IP addresses often changes across sessions or devices, increasing the likelihood of mismatches.
Best practice includes:
- Using user-provided data wherever possible
- Avoiding IP-based enrichment for identity matching
- Treating inferred attributes as contextual, not identifying
Clear separation between identity and enrichment data improves match reliability.
Review Identity Mapping and Consistency
Incorrect or overlapping identity mappings are a common cause of invalid match key errors. Pageview events should follow a single, consistent identity strategy.
This involves:
- Mapping each identifier to the correct destination field
- Avoiding reuse of identity variables across unrelated parameters
- Ensuring client-side and server-side identifiers align
Ingest ID supports this by assigning a consistent first-party identifier to visitors, where consent and implementation allow.
Test PageView Events in Controlled Environments
Before pushing updates to production, test pageview events using available event-testing and debugging tools. Controlled testing helps isolate issues without affecting live data.
Focus on:
- Flagged or rejected parameters
- Ignored identifiers
- Acknowledgement responses from receiving platforms
This step ensures fixes work as expected under real conditions.
Maintain Ongoing Monitoring and Governance
Match key requirements evolve as platform policies and privacy regulations change. Regular monitoring helps prevent regressions that reintroduce errors over time.
This includes:
- Auditing, validation, and consent logic
- Reviewing schema updates
- Tracking rejected or partially processed events
With Event IQ, teams gain visibility into event flow, delivery status, and processing outcomes across destinations.
By validating match keys early, maintaining identity consistency, and monitoring event health continuously, teams can prevent invalid parameter errors from undermining attribution or reporting accuracy. Clean, governed pageview events form the foundation of reliable analytics and confident decision-making.
Also read: 10 Best Web Analytics Tools to Enhance Your Platform
Knowing When to Escalate and Get Expert Support
Some tracking issues persist even after validating schemas, correcting match keys, and aligning identity logic. When errors continue to surface or reporting remains inconsistent, escalation becomes a practical step to protect data accuracy, not a failure in setup.
Identify When Escalation Is Warranted
If you repeatedly encounter the same pageview validation errors or see mismatches across analytics and attribution platforms despite corrective changes, the issue may stem from deeper configuration conflicts or platform-level constraints. These scenarios often require specialized review beyond routine debugging.
Provide Clear, Diagnostic Context
Productive support interactions depend on precision. When escalating, share exact error messages, affected event types, sample payloads, and any recent updates to your server-side setup. This level of detail allows faster diagnosis and reduces resolution time.
Rely on Platform-Level Guidance and Support
In environments built on server-side tracking and first-party data, support resources play a critical role in maintaining reliability. With platforms like Ingest Labs, teams have access to documentation, monitoring insights, and direct support channels that clarify validation requirements, identity-handling rules, and event-delivery behavior as standards evolve.
Escalating at the right moment ensures persistent issues are addressed efficiently and helps keep event tracking stable, accurate, and dependable over time.
Conclusion
The “server sending invalid match key parameters for PageView event” error indicates gaps in identity handling, schema alignment, or consent enforcement within server-side tracking. If left unresolved, it can disrupt attribution, fragment user journeys, and reduce confidence in analytics outputs.
Addressing this starts with auditing match keys, standardizing hashing and identity rules, and enforcing a schema-governed event model. Adding monitoring and validation at the server layer helps detect issues early, before they affect reporting or optimization decisions.
Platforms built for privacy-first analytics simplify this process. With Ingest IQ supporting server-side validation, Ingest ID maintaining consistent first-party identifiers, and Event IQ providing end-to-end event visibility, teams can reduce identity errors and maintain reliable pageview tracking at scale.
Learn how Ingest Labshelps teams validate identity, enforce schemas, and maintain reliable server-side PageView tracking.
FAQs
1. What triggers the ''invalid match key parameters'' error?
It appears when pageview events include identifiers or identity parameters that don't conform to the receiving platform's expected formats, hashing requirements, or consent rules.
2. Can improper hashing cause this error?
Yes, if identifiers like emails or custom IDs are not hashed using the correct algorithm (e.g., SHA-256) or normalized beforehand, they can be rejected at validation.
3. Does this error mean the event never reached the destination?
Not always. The event may arrive but fail identity matching or attribution processing, leading to incomplete reporting even though the event technically fired.
4. How do consent signals affect match key parameters?
Consent state governs whether certain identifiers can be attached to events. If consent is absent or conflicting, sending these identifiers can cause rejection or partial event processing.
5. Is schema enforcement essential to fixing this error?
Yes. A consistent, schema-governed event model ensures that match keys are placed correctly, use the correct data types, and comply with platform expectations, reducing the likelihood of validation errors.