Every marketing team wants to know which campaigns actually drive results. The key to answering that question lies in attribution tags, small pieces of information added to your URLs or tracking systems that reveal where each lead or conversion came from.
When used effectively, attribution tags can transform scattered marketing data into actionable insights, allowing you to measure return on investment with confidence. But if implemented incorrectly, they can just as easily distort your analytics and mislead your strategy.
This guide explains what attribution tags are, how to set them up correctly, and how modern solutions make tracking more accurate in a privacy-first, cookieless world.
Key Takeaways
- Attribution tags are small but powerful; they connect every click, ad, or email to measurable business outcomes.
- The best results come from consistent naming, privacy-compliant setup, and accurate tracking infrastructure.
- Server-side, first-party tracking now replaces traditional cookie-based tagging to ensure reliability and compliance.
- With Ingest Labs’ tools: Ingest IQ, Ingest ID, and Event IQ, businesses can maintain clean, accurate, and actionable attribution data across every channel.
What Are Attribution Tags: Definition and Importance
Attribution tags are identifiers embedded within a URL or tracking system to help marketers determine where web traffic, conversions, or leads originate.
They connect a specific campaign, platform, or user interaction to measurable outcomes, such as purchases, sign-ups, or downloads.
Common forms include:
- UTM parameters (e.g., utm_source=facebook, utm_medium=cpc)
- Tracking pixels or scripts
- Custom event tags for analytics or CRM integrations
Essentially, they are the foundation of digital marketing attribution, the process of linking actions (like ad clicks) to results (like form completions).
Why Attribution Tags Matter
Attribution tags enable marketers to:
- Identify high-performing campaigns: Know exactly which ads or posts generate conversions.
- Allocate budget efficiently: Invest more in channels that bring measurable results.
- Compare platforms: Track and analyze performance across Google Ads, Meta, LinkedIn, and others.
- Improve campaign relevance: Tailor content and targeting based on user behavior insights.
Without proper tagging, campaign data becomes fragmented, making ROI analysis nearly impossible.
Example: A retail brand discovered that 40% of its “organic” sales were actually from untagged paid influencer campaigns, a costly blind spot fixed by structured UTM tagging.
Core Components of Attribution Tags
| Tag Element | Purpose | Example |
| Source | Identifies where traffic originates | utm_source=google |
| Medium | Defines the marketing channel | utm_medium=email |
| Campaign | Names the specific campaign | utm_campaign=spring_sale |
| Content | Distinguishes multiple links in the same campaign | utm_content=cta_button |
| Term | Tracks paid search keywords | utm_term=server-side-tracking |
The Shift to Data Accuracy and Privacy
As browsers limit cookies and third-party tracking, traditional attribution methods have become less reliable. Attribution tags now need to work hand-in-hand with first-party data systems that store and process tracking events directly on your server.
This is where Ingest Labs brings value, by capturing and managing attribution data server-side via Ingest IQ and Event IQ, ensuring that tags remain accurate and compliant even when user data policies tighten.
Also Read: Finding Ways for Effective Attribution Measurement in Digital Marketing
Common Types of Attribution Tags (UTMs, Pixels, Custom Tags)
Attribution tags come in different forms depending on your tracking setup. Each serves the same purpose, identifying where traffic and conversions originate, but functions differently based on the data ecosystem.
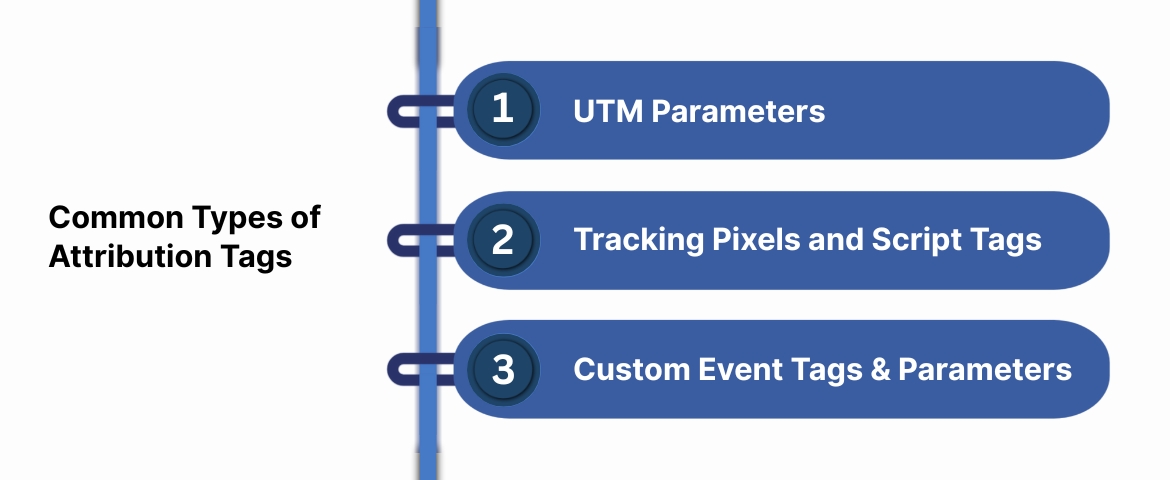
1. UTM Parameters (Most Common Form)
UTM (Urchin Tracking Module) parameters are snippets added to a URL. They tell analytics tools how a visitor reached your website.
Example:
What they track:
- Source: platform sending traffic (e.g., LinkedIn, Google).
- Medium: channel type (CPC, email, referral).
- Campaign: specific marketing initiative.
- Content/Term: ad variations or keywords.
Benefits:
- Simple to create and analyze.
- Supported by all analytics platforms.
- Excellent for paid ads, email marketing, and influencer links.
Limitations:
- Manual errors (misspellings or inconsistencies).
- Can’t identify the same user across multiple sessions.
- Vulnerable to cookie loss or private browsing.
Tip: Centralize tag creation using a shared UTM naming sheet to maintain consistency across teams.
2. Tracking Pixels and Script Tags
Tracking pixels are small pieces of code embedded in web pages or emails. When a user visits or interacts, the pixel fires and sends event data to the analytics platform.
Common types:
- Conversion pixels (Google Ads, Meta Pixel).
- Retargeting pixels for ad audiences.
- Email open pixels for campaign performance.
Why they matter:
- Automate tracking without modifying URLs.
- Enable retargeting and event-based conversions.
- Capture behavior that doesn’t rely on link clicks.
Challenge: Traditional pixels rely heavily on browser storage (cookies). As privacy rules and ad blockers expand, server-side tracking (like Ingest IQ) ensures these events are recorded reliably at the server level.
Also Read: Understanding Pixel Tags: Functionality and Usage
3. Custom Event Tags and Parameters
Advanced teams often design custom tags to track specific actions, such as video views, form completions, or chat interactions.
Example:
{
"event": "form_submit",
"category": "lead_acquisition",
"label": "contact_form"
}
Benefits:
- Full flexibility for unique user journeys.
- Ideal for web apps, SaaS platforms, and multi-touch funnels.
- Integrates seamlessly with Event IQ for real-time analytics and AI-driven insights.
When to Combine Tag Types
| Scenario | Best Approach |
| Multi-channel ad campaigns | UTM + pixel tracking |
| Product demo sign-ups | Custom event tag + server-side tracking |
| Email marketing | UTM + open pixel |
| Retargeting audiences | Pixel or API-based conversion event |
| Data compliance priority | First-party server-side tagging (Ingest Labs setup) |
Also Read: Understanding Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) in Marketing
How to Set Up URL Attribution Tags (UTM Parameters): Best Practices
UTM tagging is simple, yet inconsistent tagging remains one of the biggest causes of poor attribution. Here’s how to set up a clean, standardized, and scalable tagging framework.
1. Follow a Consistent Naming Convention
Define a shared structure for your UTM parameters before launching any campaign.
Example template:
| Parameter | Format Example | Notes |
| Source | utm_source=linkedin | Always lowercase, use the platform name |
| Medium | utm_medium=cpc | Match the advertising channel |
| Campaign | utm_campaign=product_launch_q1 | Use underscores, not spaces |
| Content | utm_content=cta_button_a | Use for ad or creative variants |
| Term | utm_term=server_tracking | Use only for paid search |
Pro tip: Automate UTM creation with a simple spreadsheet or tag builder tool shared across teams.
2. Tag Only External Links
UTMs are designed to track incoming traffic from external campaigns. Never use them on internal website links; doing so can overwrite the source, causing inaccurate attribution.
Keep Tags Short, Clear, and Logical
Avoid unnecessary complexity.
- Use lowercase letters only.
- No special characters or spaces.
- Limit campaign names to 30 characters.
Good example:
✅ utm_campaign=spring_promo
Bad example:
❌ utm_campaign=Spring%20Promo%202025!
3. Validate Tags Before Launch
Always test each tagged URL in a private browser or sandbox environment to ensure parameters register correctly in your analytics platform.
If your team uses server-side tracking, confirm that events are firing both client-side and server-side to maintain full data visibility.
4. Use Dynamic Tagging for Large Campaigns
For high-volume ad campaigns, use dynamic parameters.
Example (Google Ads):
?utm_source=google&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign={campaignid}&utm_term={keyword}
This approach automatically replaces placeholders with real values, reducing manual errors.
Ingest Labs Insight: When UTM data flows into Event IQ or Ingest ID, it merges with first-party identifiers, allowing you to attribute each conversion accurately even when cookies or sessions expire.
Also Read: Understanding Cross-Device Attribution: A Complete Guide
Tagging Mistakes That Can Break Your Data: What to Avoid
Even small tagging errors can cause major discrepancies in attribution data. Inconsistent parameters, misplaced tags, or overlooked URLs can distort your analytics and mislead your marketing strategy.
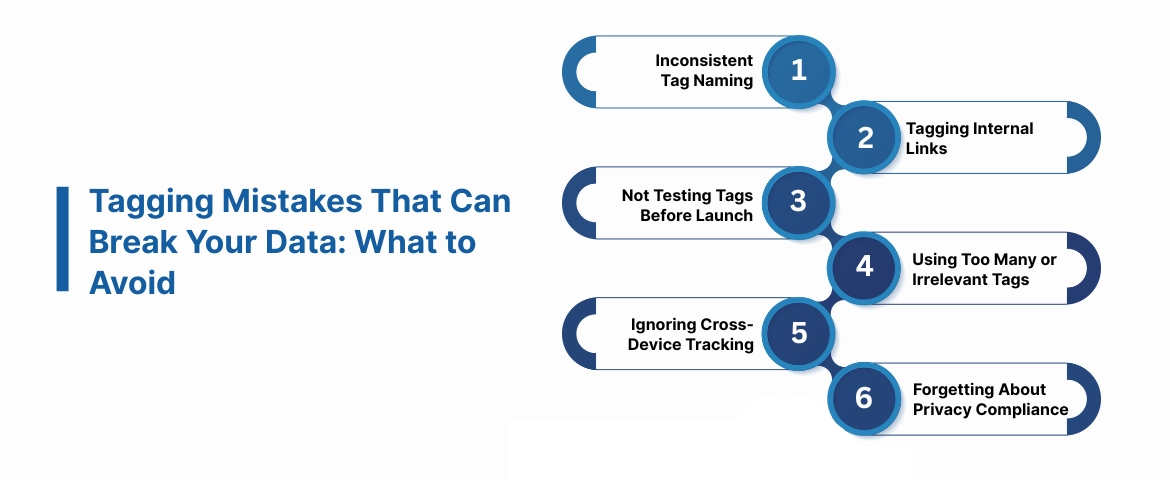
Here are the most common mistakes teams make, and how to fix them:
1. Inconsistent Tag Naming
When different team members use different naming conventions (e.g., utm_medium=CPC vs utm_medium=paid), your analytics platform treats them as separate entries.
Avoid this by:
- Creating a centralized tagging policy or UTM template.
- Keeping all tags lowercase and consistent.
- Using underscores (_) instead of spaces for readability.
2. Tagging Internal Links
Adding UTM tags to links within your own website resets the attribution chain. The user’s original source gets replaced by a false “self-referral.”
Example: A visitor from a Facebook ad clicks through to a blog post. You add UTM tags to a CTA button linking to your product page. The analytics tool now attributes that conversion to your own site instead of Facebook.
Fix: Tag only external campaign URLs, never internal ones.
3. Not Testing Tags Before Launch
Failing to test tags before running campaigns can lead to broken tracking URLs or missing data.
Checklist:
- Test tagged URLs in incognito/private mode.
- Verify they redirect correctly, and parameters appear in the browser bar.
- Use analytics tools like Event IQ to confirm that conversion events fire as expected.
4. Using Too Many or Irrelevant Tags
Over-tagging can clutter reports and make it harder to extract insights. Stick to what matters; source, medium, campaign, and content are enough for most campaigns.
Example: Instead of:
utm_source=google&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=summer_sale&utm_content=ad1&utm_term=shorts&utm_region=US&utm_audience=retargeting&utm_version=beta
Use:
utm_source=google&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=summer_sale&utm_content=ad1
5. Ignoring Cross-Device Tracking
A user might click an ad on mobile but convert later on desktop. Without a proper tracking infrastructure, this looks like two separate users, skewing attribution.
Solution: Use first-party identity resolution tools such as Ingest ID to link multiple sessions to the same individual securely. This ensures your attribution remains accurate, even across devices or browsers.
6. Forgetting About Privacy Compliance
Using tags without clear consent collection or transparent policies can breach privacy regulations.
Best Practice:
- Always disclose tracking in your privacy policy.
- Obtain user consent before storing identifiers.
- Use server-side, first-party solutions (Ingest IQ) to maintain compliance.
Also Read: Introduction to What Tag Management is and Solutions You Should Consider
Attribution Tags vs Attribution Models & Tracking Infrastructure: What’s the Difference
Many marketers confuse attribution tags with attribution models and tracking systems. While these terms sound similar, they play very different roles in the marketing measurement ecosystem.
Attribution Tags – The Data Input Layer
Attribution tags collect raw campaign data, telling you where traffic came from.
They are the “labels” attached to URLs and interactions.
- They do not decide which channel gets credit for conversions.
- They only record traffic sources.
Example: A UTM tag might say a conversion came from utm_source=linkedin, but it’s the attribution model that determines how much credit LinkedIn receives.
Attribution Models – The Decision Layer
Attribution models determine how credit is assigned across different touchpoints.
Common models include:
| Model | How It Works | Best Used For |
| First-Click | Gives 100% credit to the first touchpoint | Awareness campaigns |
| Last-Click | Gives 100% credit to the last interaction | Direct-response efforts |
| Linear | Distributes credit evenly across all touches | Multi-channel nurturing |
| Time Decay | Gives more credit to recent interactions | Short purchase cycles |
| Data-Driven | Uses AI or algorithms to assign weight dynamically | Advanced, large-scale setups |
Ingest Labs Advantage: Event IQ supports data-driven attribution, analyzing complete user journeys to assign credit accurately using first-party data, ensuring privacy and precision.
Tracking Infrastructure: The Foundation Layer
This is where data accuracy is won or lost. A strong tracking infrastructure ensures that tags and models function correctly, even when browser-based tools fail.
Key capabilities of a reliable infrastructure:
- Server-side event tracking to bypass cookie restrictions.
- Identity resolution to unify multiple sessions per user.
- Cross-channel integration (web, app, CRM, ad platforms).
- Privacy compliance is baked into every step.
Also Read: Navigating Attribution in a Cookieless and Privacy-First World: A Comparative Analysis
Privacy, Compliance, and Tagging in a Cookieless Environment
As privacy regulations evolve and browsers restrict third-party cookies, traditional tagging methods face new challenges. Attribution tags must now work within stricter compliance frameworks while maintaining accuracy and user trust.
The Changing Landscape of Data Privacy
Modern marketers operate under growing scrutiny:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) in the U.S.
These developments make browser-based tracking less reliable; many conversions go unrecorded because tags cannot fire correctly without cookies.
Why Client-Side Tagging Is No Longer Enough
Traditional client-side tagging depends on a user’s browser to send data. When cookies are blocked or deleted, tracking breaks.
Limitations include:
- Lost conversion data from ad blockers and privacy browsers.
- Inaccurate cross-device attribution.
- Dependency on user consent before every tag fires.
This not only impacts accuracy but can also increase compliance risk if consent isn’t properly managed.
The Solution: First-Party, Server-Side Tagging
Server-side tagging allows data to be collected and processed on your business’s own server instead of the user’s browser. This means attribution tags, such as UTMs, custom events, or campaign parameters, send data securely and reliably, even when cookies are limited.
Key Advantages:
- Privacy-first compliance: tags trigger only after valid consent.
- Accurate attribution: data captured directly from your server, not the browser.
- Cross-device tracking: unify multiple user sessions with one first-party ID.
- Data ownership: your business, not ad platforms, controls all lead and conversion data.
Building Consumer Trust Through Transparency
Consumers increasingly value transparency. Marketers who explain why data is collected and how it improves their experience see higher engagement rates.
Best Practices:
- Publish a clear privacy policy that mentions attribution tracking.
- Use cookie banners or consent management platforms.
- Offer users control over what’s collected.
- Regularly audit tag firing and consent behavior.
Tools like Event IQ support automated compliance management, ensuring all event tags align with regional data laws.
Also Read: Why tagging needs to move to server side
Audit, Maintenance, and Reporting: Ensuring Tag & Tracking Health
Setting up attribution tags is only the first step. The true challenge lies in maintaining data hygiene and ensuring that all tags continue to function as intended across evolving campaigns, websites, and tools.

1. Regular Tag Audits
Performing scheduled audits prevents data loss and keeps attribution reports trustworthy.
Audit checklist:
- Confirm all campaign URLs contain correct UTM parameters.
- Validate that no internal links use UTMs.
- Check for broken or duplicated tracking pixels.
- Ensure consent-based tags trigger correctly after user approval.
- Test cross-device and cross-browser event consistency.
Ingest IQ supports automated tag monitoring, notifying your team if any tracking signals fail or misfire.
2. Report and Analyze Key Attribution Metrics
Track these metrics consistently to evaluate attribution accuracy:
| Metric | Why It Matters | Tools to Monitor |
| Attributed Conversions | Confirms if tags are firing correctly | Event IQ, GA4 |
| Unattributed Sessions | Detects broken tags or missing parameters | Ingest IQ |
| Channel Contribution | Identifies top-performing campaigns | Event IQ |
| Conversion Lag | Shows how long users take to convert | CRM + Analytics |
| Cross-Device Conversions | Measures unified tracking success | Ingest ID |
Consistent reporting ensures your marketing decisions are backed by verified, first-party data.
3. Train Teams for Tag Consistency
Human error is still the number one cause of tracking breakdowns.
Training essentials:
- Share a standardized UTM and tag-naming document.
- Assign a data steward or marketing ops role for verification.
- Revisit best practices quarterly as tools and channels evolve.
4. Clean Up Legacy Tags
Old or unused tags can clutter dashboards, slow websites, and distort attribution data.
Regularly remove:
- Deprecated UTM parameters.
- Outdated tracking pixels from old platforms.
- Duplicate scripts from overlapping campaigns.
Ingest Labs Tip: Using Event IQ’s tag orchestration view helps identify redundant or inactive tags instantly.
Also Read: Best Marketing Attribution Tools and Technology Guide
How a Robust Tracking System (Like Ingest Labs) Enhances Tag-Based Attribution
Attribution tags alone cannot guarantee data accuracy; they need the right infrastructure. Ingest Labs strengthens every step of the process, ensuring tags translate into meaningful insights rather than fragmented data.
Scalable, Privacy-First Infrastructure
All three products — Ingest IQ, Ingest ID, and Event IQ — integrate into a cohesive system designed for the future of digital marketing.
| Challenge | Ingest Labs Solution | Outcome |
| Browser-based tracking loss | Server-side tracking via Ingest IQ | Accurate event capture |
| Data fragmentation | Unified identity via Ingest ID | Cohesive user journey |
| Delayed or inaccurate insights | Real-time analytics via Event IQ | Faster optimization |
| Privacy regulations | Built-in GDPR & CCPA compliance | Safer data handling |
Why This Matters for Your Business
By combining accurate tagging with reliable infrastructure, Ingest Labs empowers your team to:
- Attribute every conversion correctly.
- Prove marketing ROI with confidence.
- Operate transparently and compliantly.
- Scale lead acquisition without losing visibility.
Attribution tags tell the story. Ingest Labs ensures every chapter is recorded accurately.
Conclusion
Accurate marketing attribution begins with properly implemented tags, but it does not end there.
Attribution tags are only as powerful as the infrastructure that supports them. In today’s privacy-first world, businesses need systems that ensure every tagged click, view, or form submission is tracked, stored, and analyzed ethically and accurately.
Ingest Labs simplifies that complexity.
- Ingest IQ ensures every conversion is captured, even when cookies fail.
- Ingest ID connects sessions into a single, privacy-compliant customer view.
- Event IQ delivers real-time attribution reports that reveal what truly drives ROI.
If you want to make every marketing dollar measurable and every lead traceable, now is the time to modernize your tracking stack.
Book a Demo to see how accurate attribution transforms marketing into measurable growth.
FAQs
1. Are attribution tags and UTM tags the same thing?
Almost. UTM tags are a type of attribution tag focused on URL tracking. Attribution tags also include tracking pixels and custom event parameters used for conversions or engagement tracking.
2. Do attribution tags violate privacy laws?
No, as long as they are implemented within a consent-based, first-party framework. Using server-side tracking tools like Ingest IQ ensures compliance with GDPR and CCPA while maintaining data accuracy.
3. What happens if I forget to tag a campaign?
The campaign’s traffic will appear as “direct” or “unassigned” in analytics, making ROI measurement difficult. This is why automation and tag audits are crucial.
4. How often should I audit my attribution tags?
Every 4–6 weeks, or immediately after launching new campaigns. A quarterly deep audit is recommended to catch outdated or conflicting tags.
5. Can I rely only on Google Analytics for attribution?
Not entirely. Browser restrictions and cross-device interactions often cause data gaps. A server-side attribution platform like Event IQ complements Google Analytics by ensuring nothing gets lost between devices or sessions.
6. What’s the biggest mistake marketers make with attribution tags?
Treating tagging as a one-time setup. In reality, attribution tagging must evolve alongside your campaigns, platforms, and privacy requirements.