Tracking customer behavior across multiple devices and sessions can feel like a constant challenge for your marketing team. In fact, projections for 2025 estimate that the average person will have around 9 connected devices, amplifying the risk of fragmented data. Without a clear way to identify your audience, it becomes difficult to understand customer interactions, measure campaign impact, and avoid missed opportunities or wasted ad spend.
A User ID provides a reliable solution by tying individual interactions together across devices, sessions, and platforms. With a properly implemented User ID strategy, you can gain a unified view of your customers, understand their journey more accurately, and make data-driven decisions that improve engagement and return on ad spend. By adopting this approach, your team can build campaigns that truly resonate with your audience while maintaining compliance with privacy regulations.
In this blog, we’ll explore what a User ID is, how it works, the benefits it offers, common challenges in its implementation, and best practices.
In a nutshell:
- A User ID provides a unified, persistent identifier that tracks user behavior across devices and sessions, offering a complete view of the customer journey.
- User IDs enable accurate personalization, reliable attribution, cross-channel performance measurement, and better long-term retention analysis.
- Tracking works through steps including user identification, event tagging, cross-device unification, server-side processing, platform integration, and advanced analysis.
- Implementation requires addressing challenges like duplicate IDs, privacy compliance, and data integration, with best practices ensuring consistent, accurate, and privacy-aligned analytics.
What is a User ID in Digital Analytics?
A User ID is a unique, persistent identifier assigned to an individual user in analytics systems. It enables analytics tools to connect different interactions, whether from a phone, tablet, or desktop, back to the same person, instead of treating each session or device as a separate individual. This leads to a unified view of behavior over time.
Using a User ID allows your business to unify fragmented data, gaining a complete picture of user interactions. It forms the foundation for advanced analytics, including cohort analysis, customer journey mapping, and personalized marketing campaigns.
User ID vs. Device ID
A common point of confusion in analytics is the difference between a User ID and a device ID. While both serve to identify users, their scope and reliability differ.
A device ID is tied to a specific device or browser, meaning the same user may appear as multiple entities if they switch devices. A User ID, on the other hand, transcends devices. It links all interactions of a single user, whether they’re accessing your website from a desktop, mobile app, or tablet.
Key differences:
| Aspect | User ID | Device ID |
| Persistence | Remains consistent as long as the user is recognized or logged in | Changes when cookies are cleared, browsers change, or devices are replaced |
| Customer journey visibility | Provides a complete, unified view of the customer journey | Results in fragmented and duplicated journeys |
| Personalization capabilities | Enables consistent personalization across channels and devices | Personalization resets on new devices |
| Attribution reliability | Improves conversion and campaign attribution | Can misattribute conversions across devices |
| Privacy alignment | Supports first-party, consent-based data strategies | Often dependent on cookies or device storage |
| Impact of cookie restrictions | Less affected by browser limitations | Highly impacted by cookie loss and browser restrictions |
| Best use case | Long-term user analysis, personalization, and ROI measurement | Short-term, device-level engagement tracking |
Understanding these differences is essential for your business to achieve accurate analytics, reliable attribution, and consistent customer experiences across channels.
Also Read: What is Digital Analytics: Definition, Metrics, Data Sources, and Strategy
Next, let’s look at how User IDs improve analytics outcomes in practice.
Role of User IDs in Analytics
A User ID does more than connect sessions; it helps you understand, measure, and act on customer behavior more clearly. By linking interactions to a single identifier, you gain clarity that cookie-based tracking cannot offer.
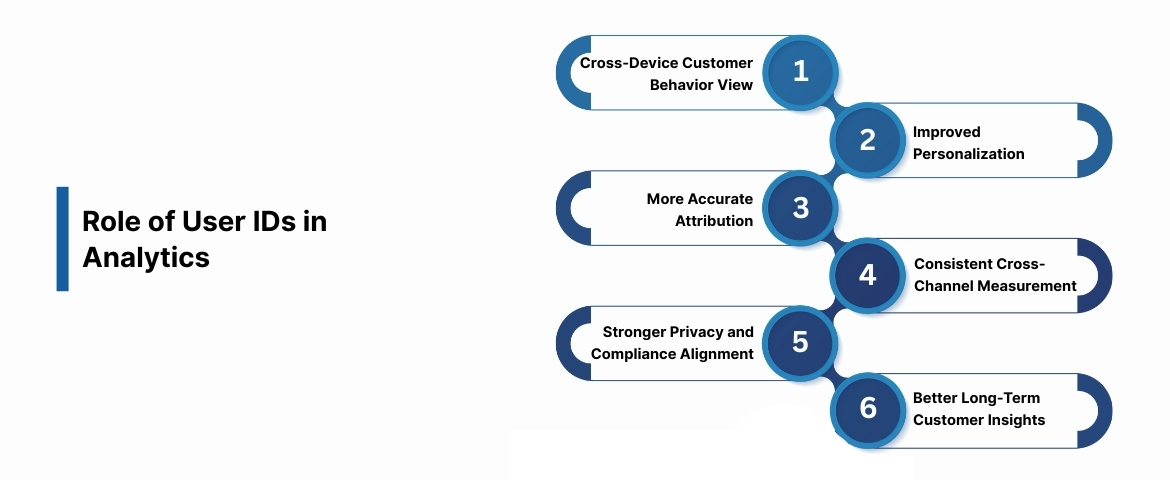
Here are the key benefits:
1. Unified View of Customer Behavior Across Devices
User ID enables you to connect a person’s activity, whether they interact on mobile, desktop, or tablet. This gives clearer insight into how users move through your digital ecosystem, preventing duplicate counts of the same individual.
Example: A shopper browsing products on their phone during lunch and completing a purchase on their laptop at home will be recognized as one user with two touchpoints instead of two separate visitors. This unified view helps you see true user engagement and conversion paths clearly.
2. Improved Personalization and Targeted Marketing
User IDs allow you to tailor experiences based on past behavior, preferences, and engagement history. This lets you send relevant messages, recommend products, and deliver content that matches user intent.
Example: An online retailer uses User ID data to recognize returning customers. It then shows product recommendations based on their previous browsing and purchases, regardless of the device. This leads to higher engagement and repeat visits.
3. More Accurate Attribution and Campaign Measurement
You can track the complete path to conversion using User IDs, even when users switch devices or return over multiple sessions. This helps you measure each channel’s contribution to conversions more accurately.
Example: A digital marketing team tracks a user who clicks a paid search ad on mobile, reads an email on desktop, and converts later through a retargeting ad. The User ID connects all touchpoints, helping marketers understand which channels contributed to revenue.
4. Reliable Cross-Channel Performance Measurement
With User IDs, you can measure performance across websites, mobile apps, email campaigns, and paid media without fragmented reporting. This helps you see how channels work together instead of reviewing them separately.
Example: An advertising agency managing multiple client campaigns uses User IDs to measure how social ads influence email engagement and website conversions, helping you refine channel budgets and messaging.
5. Stronger Privacy and Compliance Alignment
User IDs rely on first-party data collected directly from users, helping you stay aligned with privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. This reduces dependence on third-party cookies while keeping your data accurate.
Example: A US-based retailer assigns User IDs only after users consent during account creation, ensuring tracking remains compliant while still supporting detailed customer analysis.
6. Better Long-Term Customer Insights and Retention Analysis
User IDs make it easier to analyze retention, lifetime value, and repeat engagement over time. This helps you understand not just how users convert, but how they stay connected with your brand.
Example: A subscription-based platform tracks renewals and feature usage using User IDs. The analytics team identifies patterns among high-retention users and adjusts onboarding flows to improve your customer lifetime value.
Understanding these benefits highlights why User IDs are becoming a standard in digital analytics. Next, we’ll see how they actually work within analytics systems.
Also Read: What Are Unique Users and How to Track Them
How User ID Works in Digital Analytics Systems?
Understanding how User ID functions within analytics platforms helps you implement it effectively. Below is a step-by-step breakdown of how User ID tracking functions in modern digital analytics systems.
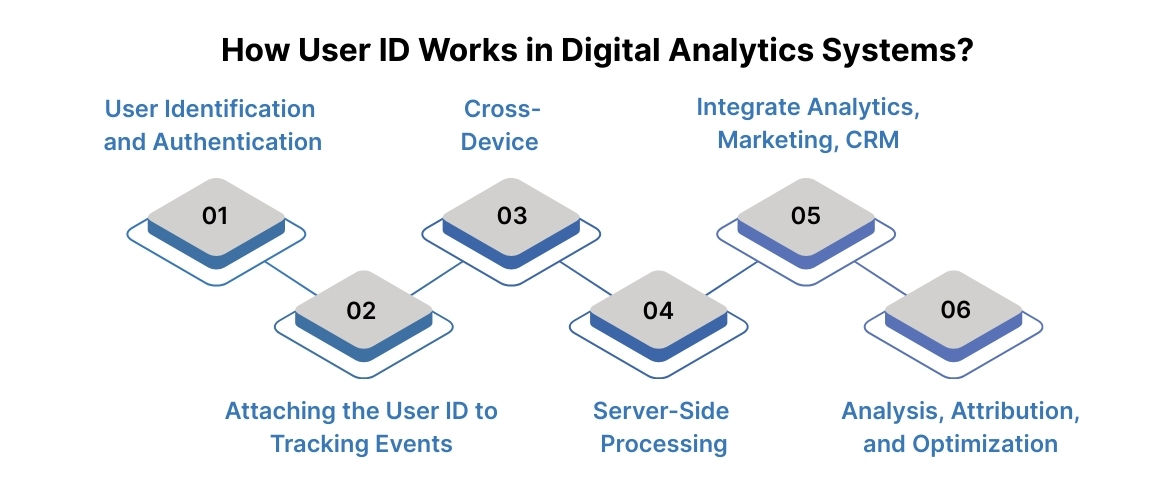
Step 1: User Identification and Authentication
User ID tracking begins the moment your system can reliably recognize a user. This usually occurs when someone performs an identifiable action, such as logging in or creating an account. At this point, the analytics system assigns a unique identifier that represents that user moving forward.
Common identification triggers:
| Identification Method | What Happens | Why It Matters |
| Account login | User signs in using verified credentials | Confirms a persistent, known identity |
| Account creation | New User ID is generated at signup | Enables tracking from the start of the relationship |
| Authenticated purchase | Checkout tied to a logged-in account | Connects revenue to a specific user |
Once assigned, this User ID becomes the reference point for all future interactions. Every tracked action can now be linked back to the same individual instead of being treated as an anonymous or session-based activity.
This step ensures analytics starts with a reliable identity, which is essential for accurate tracking across systems.
Step 2: Attaching the User ID to Tracking Events
After identification, the User ID must be passed consistently with every tracked event. This ensures that actions taken by the same user are recognized as part of a single journey, regardless of where or how those actions occur.
Events commonly linked to a User ID include:
- Engagement actions: Page views, button clicks, video plays.
- Commerce actions: Product views, add-to-cart events, purchases.
- Lifecycle actions: Sign-ups, renewals, cancellations, upgrades.
These events are sent to your analytics systems with the User ID attached as a parameter. When done correctly, the analytics platform does not treat each event as isolated behavior but as part of a continuous timeline tied to one user.
This step is crucial because incomplete or inconsistent event tagging can break the user journey and reduce the value of User ID tracking.
Step 3: Cross-Device and Cross-Session Data Unification
One of the most valuable aspects of User IDs is their ability to unify behavior across devices and sessions. A user may browse on a mobile phone, compare options on a laptop, and convert later on a tablet. Without a User ID, these actions appear as separate users.
What unification enables:
- Cross-device recognition: Mobile, desktop, and app interactions map to one user.
- Session continuity: Multiple visits over time form a single behavioral timeline.
- Journey visibility: Awareness, consideration, and conversion stages connect clearly.
This unified view allows your analytics system to show how users actually move through your funnel, instead of presenting disconnected snapshots. For marketing teams, this clarity directly improves attribution accuracy and campaign evaluation.
At this stage, User IDs transform raw interaction data into meaningful user journeys.
Step 4: Server-Side Processing and Data Validation
Modern analytics systems increasingly rely on server-side tracking to ensure data accuracy and resilience. When User IDs are processed server-side, events bypass many of the limitations of browser-based tracking, such as ad blockers and cookie restrictions.
Server-side handling supports:
- Data reliability: Events are captured even when client-side scripts fail.
- Consistency: User IDs are validated before data is forwarded to tools.
- Security: Sensitive identifiers remain protected within controlled environments.
This approach also allows you to enforce consent logic and governance rules centrally. Events tied to a User ID are processed only when permissions are met, reducing compliance risks.
By handling User ID data server-side, you gain more dependable analytics while maintaining control over data quality and privacy.
Step 5: Integration with Analytics, Marketing, and CRM Platforms
Once User ID data is validated, it flows into downstream platforms that rely on accurate user insights. These integrations ensure that analytics does not exist in isolation but actively informs your marketing, sales, and customer engagement efforts.
Platforms commonly connected using User IDs:
- Analytics tools: For cohort analysis, retention tracking, and attribution.
- Marketing platforms: For audience segmentation and campaign activation.
- CRMs and CDPs: For unified customer profiles and lifecycle tracking.
Because the same User ID is used across systems, teams can align insights without relying on probabilistic matching. The marketing team sees the same user behavior that analytics measures, and sales teams access consistent customer histories.
This step transforms User ID tracking from a measurement tool into a business-wide data asset.
Step 6: Analysis, Attribution, and Optimization
With User ID data flowing consistently, your analytics team can move beyond surface-level metrics and focus on meaningful analysis. User-centric reporting replaces session-based assumptions, providing deeper insight into how real people engage with your business.
Key analysis enabled by User IDs includes:
- User-level attribution: Understand which channels contribute to conversions.
- Retention analysis: Measure how often users return and re-engage.
- Journey analysis: Identify friction points and drop-offs across stages.
These insights support smarter optimization decisions, from refining campaign spend to improving on-site experiences. Instead of guessing based on incomplete data, teams can act on verified user behavior.
At this final stage, User IDs deliver their full value by connecting accurate data to measurable business outcomes.
Ingest ID simplifies this process for you by integrating User IDs into your marketing stack, ensuring accurate data collection and real-time insights without heavy technical overhead.
In the next section, let's discuss the common challenges associated with user IDs.
Common Challenges with User IDs
While User IDs offer value, there are practical challenges businesses face during their implementation.
- Duplicate or Incorrect IDs: Assigning multiple IDs to a single user or incorrectly merging profiles can distort analytics, affecting your decision-making and personalization strategies.
- Privacy Compliance: North American privacy laws like CCPA impose strict requirements for consent and data handling. Mishandling User IDs can put your business at legal risk.
- Cross-Platform Integration: Combining data from multiple systems can be complex. Different platforms may use varying formats or have incomplete user information.
- Login Dependency: User ID tracking typically requires users to log in or provide identifiable information, limiting data collection for anonymous visitors.
- Data Quality and Accuracy: Inconsistent or duplicate User IDs can lead to inaccurate analytics, affecting decision-making and attribution models.
- Technical Expertise: Configuring analytics systems, tagging mechanisms, and integrations often requires specialized knowledge, making implementation harder without technical support.
To overcome these challenges, you should follow best practices when implementing User ID tracking.
Best Practices for Implementing User IDs in Digital Analytics
To harness the full potential of User IDs, businesses should follow these best practices:
- Use First-Party Identifiers: Rely on data you control, such as login credentials, hashed emails, or CRM IDs, to minimize reliance on third-party cookies.
- Ensure Privacy Compliance: Collect and manage consent, anonymize sensitive data when required, and align your User ID strategy with CCPA/GDPR regulations.
- Leverage Server-Side Tracking: Capture interactions at the server level to maintain continuity across devices and avoid data loss from browser limitations.
- Maintain Consistent User IDs: Ensure each user has a single, persistent identifier across platforms to prevent data fragmentation.
- Integrate Across Systems: Connect User ID data with analytics tools, marketing automation platforms, and CDPs for a complete view of the customer journey.
- Regularly Audit Data Quality: Check for duplicates, incomplete profiles, or mismatched IDs to maintain accurate analytics.
- Educate Teams and Stakeholders: Ensure marketing, analytics, and IT teams understand how User ID tracking works, its limitations, and its benefits.
With these practices in place, you can fully capitalize on User IDs to improve personalization, attribution, and campaign performance.
How Ingest Labs Can Help Streamline User ID Tracking?
Ingest Labs provides privacy-first, data-driven solutions to help businesses implement User ID tracking seamlessly. Their suite of tools simplifies cross-device tracking, analytics, and personalization without requiring extensive technical expertise.
Here’s how we can assist you:
- Ingest ID for Accurate Attribution: Assigns unique first-party identifiers to users, enabling precise tracking across sessions and devices while maintaining privacy compliance.
- Ingest IQ for Server-Side Tracking: Captures data accurately, bypassing browser limitations, and streams it to analytics and CDP platforms for actionable insights.
- Event IQ for Unified Analytics: Aggregates data from multiple sources, leverages AI for trend detection, and helps marketers deliver consistent experiences across channels.
- Seamless Integration with Marketing Tools: Ingest Labs ensures User ID data flows smoothly to CRM systems, personalization engines, and email platforms, enabling consistent and targeted campaigns.
- Privacy Compliance Made Easy: All tools are designed with GDPR and CCPA compliance in mind, helping businesses maintain ethical data practices without compromising analytics capabilities.
By integrating these solutions, businesses can gain actionable insights, enhance personalization, and optimize marketing performance.
Conclusion
A User ID in digital analytics is more than just a tracking tool; it is a foundation for understanding your users across devices, sessions, and channels. By moving beyond device-based tracking, businesses gain a comprehensive view of user behavior, improve personalization, and optimize marketing performance.
Implementing a robust User ID strategy requires careful planning, privacy compliance, and technical integration. However, by following best practices and utilizing solutions like Ingest Labs, organizations can simplify implementation, ensure accurate analytics, and deliver actionable insights.
Contact us today to explore how Ingest Labs can help you implement an efficient and compliant User ID strategy tailored to your business needs.
FAQs
1. How does a User ID differ from a Client ID?
A User ID uniquely identifies a logged-in user across devices and sessions, while a Client ID tracks individual browsers or devices. User ID provides a unified view of a user’s behavior, unlike Client ID, which treats each device separately.
2. What are the requirements for a valid User ID in Google Analytics?
A valid User ID must be unique, persistent, and not contain personally identifiable information (PII). It should consistently represent the same user across sessions and devices to enable accurate cross-device tracking.
3. Can User ID track anonymous users?
No, user ID cannot track fully anonymous users. It requires a unique identifier tied to a logged-in or recognized user. Anonymous visitors are tracked using Client ID instead.
4. How does User ID improve metrics like DAU and MAU?
User ID consolidates activity across devices, preventing duplicate counts of the same user. This provides more accurate Daily Active Users (DAU) and Monthly Active Users (MAU) metrics by reflecting true user engagement.
5. How do you generate and assign a User ID?
User IDs are generated by your authentication system, often during login or account creation. They are then passed to Google Analytics via tracking code, linking user activity across sessions and devices for unified reporting.