Is the fear of a massive data fine freezing your marketing personalization efforts? You rely on Personal Identifiable Information (PII Marketing) to drive conversions, yet the regulatory environment is shifting daily, transforming PII from an asset into a significant liability.
For instance, privacy-related class-action lawsuits in the US surged30% between 2023 and 2024, signaling the escalating risk of data mismanagement. You know privacy-centric personalization increases ROI, but you need a secure, compliant method to execute it.
This blog clarifies the risks and rewards of personal data marketing, detailing essential North American compliance frameworks (CCPA, CPPA), and demonstrating the necessary data governance solutions you must implement to succeed safely in today’s high-risk environment.
Key Takeaways
- PII is any personal information that can identify someone, and using it in marketing requires following strict privacy rules.
- To stay compliant, collect only what you need, be transparent with users, and respect their choices.
- Use PII safely by securing it, limiting who can access it, and avoiding sharing raw data with outside platforms.
- Train your team regularly and review your data practices to prevent mistakes or privacy risks.
- A strong PII program requires governance, training, risk reviews, and automated monitoring.
Defining PII and Real-World Examples in the Digital Age
Personally Identifiable Information (PII) is any data that can identify, contact, or trace an individual, either by itself or when combined with other details. As smartphones, online platforms, e-commerce, and social media have grown, so has the volume of data being generated. Understanding this definition is the first step toward compliant PII marketing.
Real-World Examples of PII
To make this concrete, here is a list of common data points classified as PII:
- Full name: Including maiden name, mother’s maiden name, or aliases.
- Personal identification numbers: Like social security number (SSN), passport number, or driver’s license number.
- Financial information: Credit card numbers, bank account details, and other financial records.
- Medical records: Any information related to health status or the provision of health care.
- Biometric data: Fingerprints, retinal scans, and voiceprints.
- Contact information: Personal address, personal email, and personal phone number.
- Digital identifiers: IP addresses, cookies, and device IDs can be considered PII under regulations like the CCPA and GDPR when linked to a user.
Sensitive vs. Non-Sensitive PII
Regulators divide PII into two core categories, which are crucial for determining the level of security and consent required:
- Non-sensitive PII: This is information that is, or can be, publicly available. While it can identify a person (e.g., a work email address, ZIP code, race, or gender, etc.), its disclosure wouldn’t typically cause direct harm.
- Sensitive PII: This type of data, if exposed, misused, or accessed without permission, can cause serious harm, embarrassment, or disadvantage to the person it belongs to (e.g., Social Security number (SSN), credit card information, passport information, financial information, medical records, etc.). This type of data requires strict access controls and encryption under North American laws.
Technical Note: While non-PII (e.g., device type, browser language) cannot identify someone on its own, a string of non-PII, when combined, can sometimes become PII. This is known as the “mosaic effect,” and it is why modern data governance requires you to manage even seemingly anonymous data within a comprehensive identity framework like Ingest ID.
Why PII Compliance Is Non-Negotiable for Your Business
Treating PII compliance as a mere checkbox exercise is a critical mistake. It is a core business function that impacts everything from revenue to brand equity. Investing in a robust compliance framework is one of the smartest decisions a modern company can make. The stakes are simply too high to ignore, especially in the US and Canada.

1. Building and Maintaining Customer Trust
Consumers today pay close attention to how brands handle their personal data. They naturally prefer companies that are open about their practices and prioritize privacy. A public commitment to PII protection is a powerful differentiator that builds long-term loyalty and reduces customer churn.
2. Avoiding Costly Fines and Legal Penalties
The financial consequences of non-compliance are staggering:
- Regulations like GDPR can levy fines up to 4% of a company’s global annual revenue.
- In the US, the CCPA/California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) brings similar risks with fines of up to $7,500 per intentional violation.
These fines can cripple a business, and they don’t even include the cost of litigation and settlement fees that follow a major breach.
3. Protecting Brand Reputation and Preventing Identity Theft
A single data breach can erase years of brand building. News of a breach spreads quickly, leading to customer churn and a significant loss of public confidence. Beyond your brand, a PII breach has real human victims, as leaked data can be used for identity theft and financial fraud.
4. Gaining a Competitive Advantage
Companies that excel at PII compliance can turn it into a competitive advantage. By demonstrating a strong commitment to data privacy, you signal to the market that you are a responsible and trustworthy partner. This can attract more sophisticated customers and open doors to new business opportunities, especially in highly regulated industries.
This mandate for compliance, however, is not a barrier to growth; it is the necessary foundation for the next evolution of high-performance advertising. By establishing a robust, privacy-first framework, you transform the risk associated with PII into the trust required to gather and activate more valuable customer data.
The question then shifts from how to avoid fines to how to use this ethically secured data to drive measurable business results.
How PII is Used in Marketing: High-Value Use Cases
When managed compliantly, the use of PII directly fuels high-ROI marketing strategies that are essential for e-commerce and agency operations.
| PII Marketing Use Case | Business Benefit for You |
| Personalized Retargeting | Creating Custom Audiences (via hashed email/phone number) for highly effective re-engagement campaigns across social and display channels. |
| Lifecycle Email Segmentation | Triggering emails based on transactional history and known preferences (e.g., win-back campaigns, birthday offers). |
| Enhanced Conversions (EC) | Sending purchase records containing hashed customer PII to ad platforms to close the measurement loop and improve bidding algorithms. |
| Personalized Customer Service | Using a customer’s name, phone number, or recent order history to provide context-aware support increases satisfaction and loyalty. |
Also Read: Exploring Future Trends in Data Collection and AI Automation
Understanding where PII creates value in marketing is only half the picture. To use that data responsibly, brands must follow the core compliance principles that govern data handling across North America. The next section outlines these foundational rules.
Core Principles of PII Compliance in North America
Operating a PII marketing strategy in the US and Canada requires adherence to foundational principles mandated by laws like the CCPA/CPRA (California) and Canada’s PIPEDA.
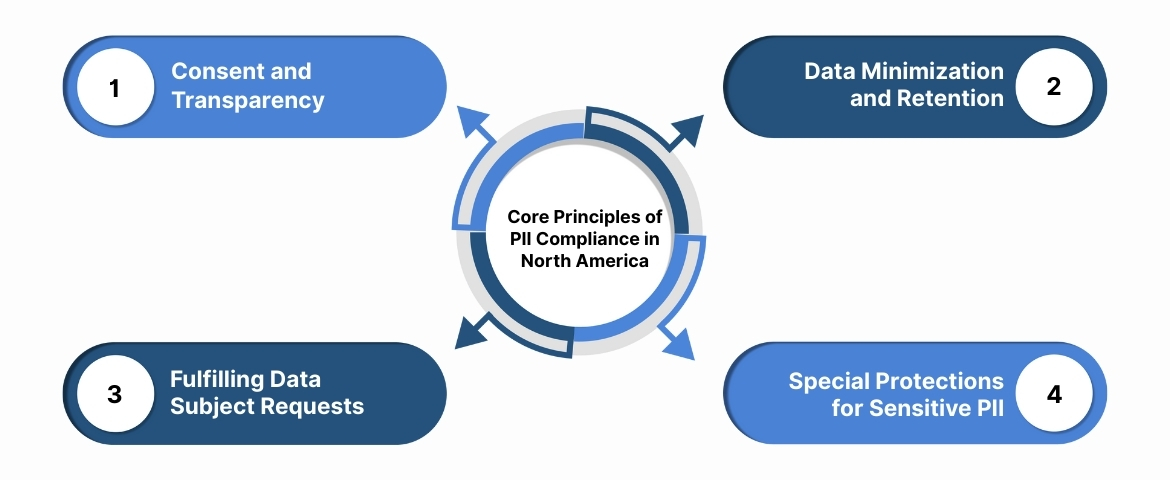
1. Consent and Transparency
You must provide clear and conspicuous notice to consumers about what PII you collect, the purposes for which you use it, and which third parties receive it.
A consent management platform (CMP) dynamically adjusts tracking by enabling or disabling cookies and scripts in real time based on the user's consent preferences, ensuring only authorized data collection occurs.
2. Data Minimization and Retention
You must limit the collection of PII to what is strictly necessary for the stated purpose. You also need clear policies on how long you retain data and how you securely delete it once the purpose has expired. This prevents unnecessary legal risk.
3. Fulfilling Data Subject Requests (DSRs)
Both CCPA/CPRA and the principles guiding PIPEDA require you to respond to consumer requests to know, correct, or delete their PII. This is technically challenging if PII is scattered across multiple marketing and analytics tools.
4. Special Protections for Sensitive PII
Sensitive PII (such as health data, precise geolocation, race, or sexual orientation) often requires a higher standard of consent ("opt-in") and is subject to greater restrictions on its use for personal data marketing.
The Global Landscape: Key PII Compliance Regulations
Moving in the web of PII regulations can feel overwhelming. For businesses operating in North America, you must understand how global standards influence US and Canadian state and federal laws.
Key Regulations You Need to Know
| Aspect | GDPR (EU) | CCPA/CPRA (California) | HIPAA (USA) |
| Primary Focus | Protecting all personal data of EU residents. | Granting privacy rights to California consumers. | a framework governing PHI in healthcare environments (not applicable to most marketing systems). |
| Who is Protected? | Any individual within the EU (“data subject”). | California residents (“consumers”). | Patients of healthcare providers (“individuals”). |
| Key Consumer Rights | Right to erasure ("right to be forgotten"). | Right to opt out of the sale/sharing of data. | Right to access and amend health records. |
These regulations create the legal boundaries for how PII can be used. For marketers, the task is turning those rules into safe, effective personalization strategies. The next section explains how to do this responsibly.
PII Compliance in Marketing: Balancing Personalization and Risk
Marketers rely on data to create personalized experiences, putting them on the front lines of PII compliance. Balancing personalized marketing with strict privacy expectations has become a major hurdle for modern marketers.
Personalization vs. Privacy: Finding the Sweet Spot
People appreciate personalization, yet they remain concerned about potential data misuse. The key is transparency and control. You must be clear about what data you are collecting and how you are using it to improve their experience. Give them easy-to-use controls to manage their preferences and opt out if they choose.
Compliant Lead Generation and Data Collection
Every web form and lead capture mechanism must be designed with compliance in mind.
- Action: Include links to your privacy policy, use clear language, and obtain explicit consent where required.
- Best Practice: Avoid pre-checked boxes and use a double opt-in process for email subscriptions to ensure consent is freely given and verifiable—a best practice aligned with PIPEDA’s emphasis on meaningful consent.
Managing PII in Marketing Attribution Models
Attribution requires tracking user journeys across multiple touchpoints, which often involves collecting identifiers that could be considered PII. It’s vital to ensure your approach to marketing attribution models is privacy-centric. This might involve using aggregated or anonymized data for analysis and ensuring that raw PII is not exposed to analysts unnecessarily.
Measuring PII Compliance and Marketing ROI
What gets measured gets managed. Monitoring the right metrics is critical for evaluating how well your compliance program works and proving its impact to leadership.
- Key Metrics for Tracking Compliance: Monitor metrics such as the number of data access requests processed, the share of employees who have finished mandatory privacy training, and the number of security incidents reported and resolved.
- Ensuring Compliant ROI Calculations: When calculating the return on investment for your marketing campaigns, you must do so in a compliant manner. This means ensuring your ROI calculations do not rely on the improper use of PII. For instance, reports shared with wider audiences should use aggregated, non-identifiable data to demonstrate performance without exposing individual customer details.
Utilizing Automated Reporting Solutions for Oversight
Manual compliance checks are prone to error and are not scalable. Using automated reporting solutions, such as those within Event IQ, can provide continuous monitoring of your data environment. These tools can flag potential compliance issues in real time, allowing you to address them before they become serious problems.
Also Read: Best Practices for Handling PII Data
Best Practices for Handling PII: Do’s and Don’ts
Daily habits and processes are what truly define a company’s commitment to privacy. This table outlines practical guidelines for employees handling PII:
| Do | Don’t |
| Do use secure, internal links or unified platforms (Event IQ) to share data, never sending raw PII via unencrypted email attachments. | Don’t store PII locally on personal computers, laptops, or mobile devices; always use secure, cloud-based systems with restricted access. |
| Do use data minimization principles; only access or collect the minimum PII necessary to perform a specific job function. | Don’t reuse passwords or share login credentials for PII-accessing systems. |
| Do verify a user’s identity before acting on a Data Subject Request (DSR) to prevent unauthorized deletions or data access. | Don’t mix sensitive PII (like credit card numbers) with non-sensitive PII in the same, unprotected database field. |
| Do ensure PII is pseudonymized or hashed (using tools like Ingest IQ) before it is transferred to any external advertising platform. | Don’t bypass the established consent management framework or ignore user opt-out signals, even if the data appears anonymized. |
While daily best practices help maintain safe data handling, organizations must still address broader structural challenges. The next section breaks down the major obstacles that impact PII compliance in marketing.
Key Challenges in Achieving PII Compliance and How to Address Them
A successful PII strategy in marketing begins with identifying the core challenges that often hinder compliance across modern data environments.
| Challenge | Description | Solution |
| Data Sprawl & Fragmentation | Organizations gather large volumes of data across many tools and storage systems, making it hard to locate and secure all PII. | Use automated data-discovery tools and consolidate information into a centralized, governed environment to create a single, reliable source of truth. |
| Constantly Changing Regulations | Privacy laws evolve quickly, and global businesses must manage different rules across multiple regions, increasing compliance complexity. | Assign a dedicated compliance lead or team to monitor legal updates. Build flexible policies that can adapt as regulations shift. |
| Secure System Integration | PII often moves between CRMs, analytics platforms, and marketing systems. Each transfer point introduces security risks, especially in legacy setups. | Implement a secure, modern integration platform to manage data flows with encryption, access controls, audit logs, and automated monitoring to prevent unauthorized access. |
| Low Employee Awareness | Mistakes like mishandling files or falling for phishing attempts remain major causes of data breaches, even with strong tech safeguards. | Provide continuous, role-specific training. Conduct routine phishing tests and reinforce a workplace culture where everyone recognizes their responsibility in safeguarding PII. |
Want to reduce compliance risk with smarter data workflows for marketing? Learn how Ingest Labs keeps your PII protected across every system. Contact us to know more.
With the core compliance challenges addressed, it’s time to translate those principles into marketing practice.
Addressing Challenges in PII Compliance in Marketing
Achieving and maintaining compliance with laws like CCPA/CPRA and PIPEDA presents specific, complex operational hurdles for medium- to large-sized enterprises. Recognizing these challenges is the first step toward implementing a robust technical solution.
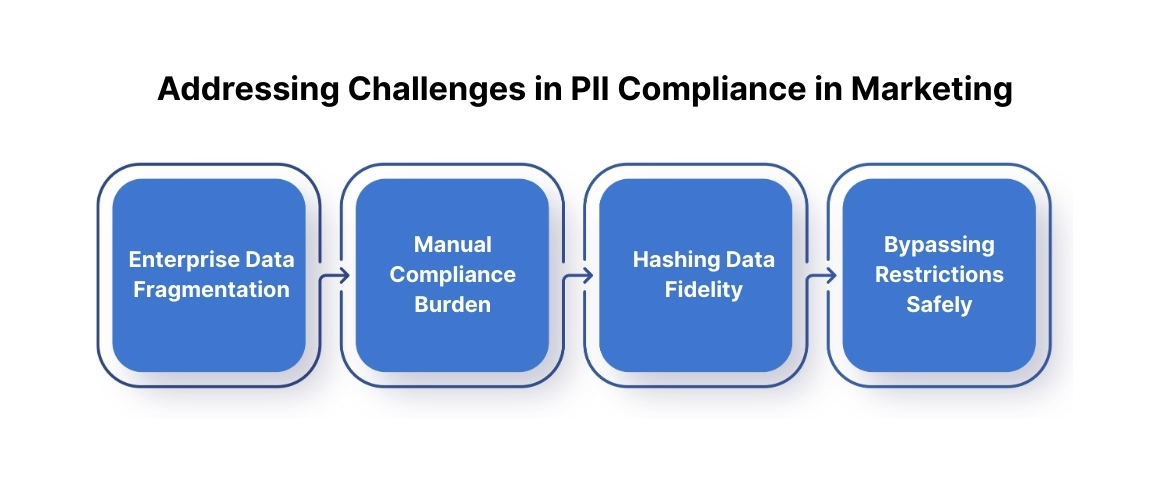
1. Data Fragmentation Across the Enterprise
Challenge: PII resides in numerous silos, CRM, ERP, marketing automation tools, cloud warehouses, and client-side web tags. This makes it nearly impossible to maintain a single, consistent record of consent or to accurately fulfill a Data Subject Request (DSR).
- Impact: High operational cost, inconsistent compliance policy enforcement, and increased risk of a data breach.
2. The Technical Burden of Manual Compliance
Challenge: Manual processes, such as tracking consent status via spreadsheets or fulfilling DSRs by hand across multiple systems, are error-prone and cannot scale with business growth or increasing data volume.
- Impact: Slow DSR fulfillment (violating regulatory deadlines) and high personnel costs.
3. Maintaining Data Fidelity During Hashing
Challenge: To comply with security mandates, PII must be pseudonymized (e.g., hashed) before being sent to ad platforms for PII marketing. If the hashing process is inconsistent, delayed, or done client-side, the resulting hashed ID is inaccurate, leading to low match rates and wasted ad spend.
- Impact: Inaccurate attribution and reduced Return on Ad Spend (ROAS).
4. Bypassing Browser and Ad-Blocker Restrictions
Challenge: Privacy-enhancing technologies (like ITP and ad-blockers) restrict client-side tracking, causing PII collection and consent signals to be lost.
- Impact: Incomplete conversion data, leading to flawed campaign optimization and non-compliance if consent signals are missed.
With the major obstacles identified and addressed, the next step is implementing a consistent framework that your team can follow. This practical checklist breaks PII compliance into clear, manageable steps for daily operations.
Is your current PII marketing strategy compliant with CCPA/CPRA and PIPEDA? Fragmented data poses a major risk. Discover how Ingest Labs’ integrated platform supports more consistent event handling and identifier propagation within your governance framework. Request a demo to secure your compliance framework.
A Seven-Step Practical Checklist for PII Compliance in Marketing
Protecting personal data requires an organized, ongoing approach and not a one-time task. Use this seven-step checklist to build and maintain a strong, sustainable compliance program for marketing.
Step 1. Identify and Classify All PII
Start by mapping where PII exists across your systems. Run a full discovery audit to locate every database, tool, and workflow that collects or processes personal data. Label each data type as sensitive or non-sensitive so you can prioritize protections.
Step 2. Create a Clear PII Governance Framework
Once you know what data you have, define how it should be managed. Develop a governance policy that outlines responsibilities, approved handling procedures, and lifecycle rules. Make sure this documentation is accessible and understood across the organization.
Step 3. Apply Data Minimization Best Practices
Collect only the information you truly need for your business purpose. Extra data increases security and compliance risks. Review stored PII regularly and securely delete anything that falls outside your retention requirements.
Step 4. Strengthen Access Controls and Security Measures
Limit who can view personal data by enforcing role-based access and granting permissions strictly on a need-to-know basis. Encrypt PII both when stored and when transmitted to prevent unauthorized access.
Step 5. Prepare a Clear Incident Response Plan
Even with strong controls, breaches can happen. Create and practice an incident response plan that explains how to contain issues, investigate the cause, notify users and regulators, and prevent repeat incidents. Acting quickly and transparently is essential.
Step 6. Train Employees Regularly
Human error is a major risk. Provide recurring training to help employees recognize PII, follow data policies, and spot common threats such as phishing attempts.
Step 7. Run Ongoing Audits and Risk Reviews
Compliance must be continuously maintained. Conduct periodic audits and risk assessments internally and with trusted third parties to surface gaps. Use these findings to update your controls and keep pace with evolving regulations and threats.
Following these steps is crucial, but manual processes alone aren’t enough to stay compliant as data volume grows. The next section explains how Ingest Labs’ platform automates PII governance and enforces compliance across your entire data environment.
Technical Solution: How Ingest Labs Manages PII
Ingest Labs provides the integrated platform necessary to execute a compliant PII marketing strategy, turning PII management from a technical risk into an automated operational asset.
1. Ingest ID: The Compliance Identity Link
Ingest ID maintains a consistent first-party identifier when you supply a hashed login or user ID, ensuring it stays attached to the associated event data. This is the key to managing DSRs efficiently. When a user requests deletion, Ingest ID ensures the request is accurately applied to every piece of associated PII and behavioral data across all linked systems.
2. Ingest IQ: Server-Side Security for PII
Ingest IQ enables you to shift from risky client-side data transmission to secure server-side tracking.
- Hashed PII: Ingest IQ handles the secure transformation (hashing) of emails and phone numbers before sending them to platforms like Facebook Conversion API or Google Enhanced Conversions, meeting the technical security requirements for PII marketing.
- Accurate Signal Capture: By bypassing browser restrictions, Ingest IQ ensures you capture compliant consent signals and conversion events with greater accuracy than traditional tags.
3. Event IQ: PII Governance and Activation
Event IQ, helps monitor event quality and schema consistency, but it is not a Customer Data Platform and does not unify customer records.
- Consent Hub: It receives and unifies consent decisions, ensuring segments created for PII marketing are always compliant with the user’s expressed preferences.
- Simplified DSRs: Event IQ can surface event issues when configured, but consent and DSR fulfillment must be handled within your own systems.
Conclusion
The reality of PII marketing is simple: you cannot stop collecting personal data, but you must control it perfectly. The operational risk posed by fragmented PII and non-compliance with North American laws like CCPA/CPRA and PIPEDA is no longer theoretical; it directly results in multi-million dollar liabilities.
You must move beyond manual, client-side data management. By implementing a centralized system for PII governance, identity unification, and server-side tracking, you transform data liability into a scalable, compliant asset.
Stop risking fines and data breaches. Ingest Labs offers the integrated solutions, Ingest ID, Ingest IQ, and Event IQ, that give you a single, unified, and compliant framework to secure your PII marketing efforts. Book a demo today to build your privacy-first architecture.
FAQs
1: Is an IP address considered PII in North America?
Yes. IP addresses can be treated as PII under laws like CCPA/CPRA when they can be linked to a person or combined with other identifiers.
2: What is the risk of using raw (unhashed) PII in marketing?
Using unhashed data exposes customers to unnecessary risk and increases your liability. Hashing protects the data while still allowing accurate audience matching.
3: How does Ingest Labs support Data Subject Access Requests?
Ingest ID creates a unified profile, while Event IQ can help surface event-level mappings when configured, but DSR fulfillment still depends on your internal data stores and processes.
4: Does server-side tracking automatically ensure compliance?
Not on its own. Compliance also depends on your policies and consent setup. However, Ingest IQ strengthens compliance by hashing PII, honoring consent signals, and securing data server-side.
5: Can enriched PII be used for marketing without fresh consent?
Only if the enrichment purpose still aligns with the original consent. If the new data changes how you target or profile customers, an updated notice or fresh consent may be required.
6: What’s the safest way to share PII with ad platforms?
Always use hashed identifiers and send data through secure, server-side pipelines. This protects user identities while still enabling audience matching and measurement.