First-Party vs Third-Party Cookies Explained
Cookies are small pieces of data that websites store on users’ browsers to track their behavior, preferences, and more.
While most people have encountered cookies through website pop-ups asking for consent, not everyone knows that there are different types of cookies that serve different purposes: first-party cookies and third-party cookies. Understanding the distinction between the two is essential, particularly as privacy concerns and data protection regulations continue to evolve.
In this blog, we will explore first-party vs third-party cookies, their uses, differences, privacy implications, and how browsers are changing their approach to cookies in light of growing privacy concerns.
Let’s get started.
Key Takeaways
- First-party cookies are set by the website you're visiting and are used for personalizing the user experience, managing sessions, and collecting data for analytics.
- Third-party cookies are set by external domains and primarily used for tracking users across multiple sites for advertising and analytics purposes.
- Privacy concerns have led to major browsers, like Safari and Firefox, blocking third-party cookies by default.
- Regulations like GDPR and CCPA now require explicit user consent for cookie tracking.
What Are Cookies?
Cookies are small text files stored on a user's device when they visit a website. These files contain data such as user preferences, login information, and tracking data. Cookies can be classified into different categories based on their origin and usage.
First-Party Cookies: Overview and Uses
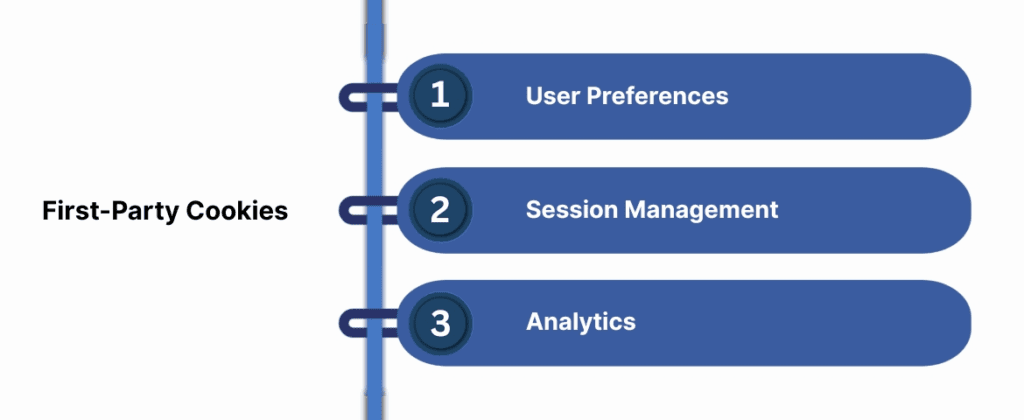
First-party cookies are set by the website the user is currently visiting. They are stored directly in the user’s browser and are only accessible by the domain that set them. These cookies are essential for enhancing the user experience on a specific site, and they are often used for the following purposes:
- User Preferences: First-party cookies help remember user settings, such as language preferences or dark mode settings, making the website experience more personalized.
- Session Management: They are used for maintaining user sessions, such as keeping a user logged in while navigating between pages.
- Analytics: First-party cookies are commonly used to gather data on how users interact with the website, such as which pages are visited and how long users stay. This information is used to improve the website’s functionality and content.
Third-Party Cookies: Overview and Use
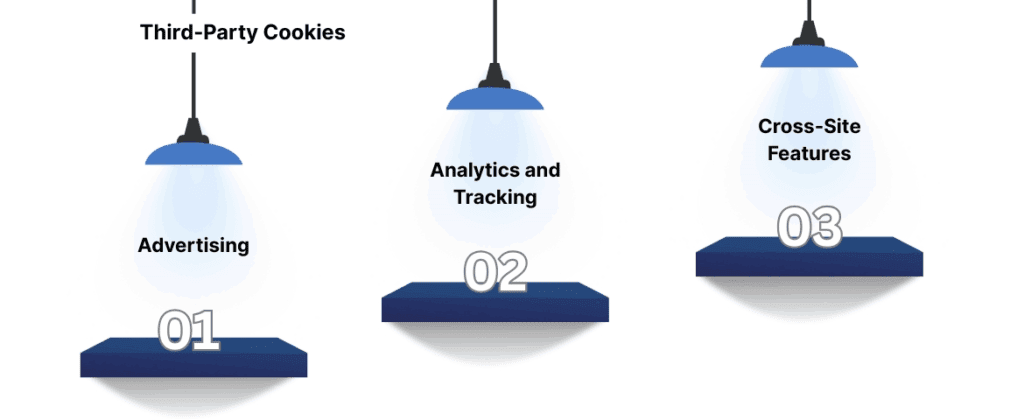
Third-party cookies are set by domains other than the one the user is currently visiting. For example, if you visit a website that has embedded YouTube videos or ads from Google, third-party cookies may be set by these external services. These cookies are often used for the following purposes:
- Advertising: Third-party cookies allow advertisers to track user behavior across different websites, creating detailed profiles that can be used for targeted ads. For example, if you visit an e-commerce site and then see an ad for the same product on a different site, it’s likely due to third-party cookies.
- Analytics and Tracking: Third-party cookies also allow external analytics services (such as Google Analytics) to track user behavior across multiple websites, giving companies a broader view of user behavior across the web.
- Cross-Site Features: Third-party cookies can enable features like social media sharing buttons, embedded content (such as videos or ads), and other elements that come from external sources.
Key Differences Between First-Party and Third-Party Cookies
While both first-party and third-party cookies are small pieces of data stored on a user's device to help websites function more effectively, they serve different purposes and have unique privacy implications. Let’s take a closer look at the differences between these two types of cookies.
| Feature | First-Party Cookies | Third-Party Cookies |
| Origin | Set by the website the user is visiting. | Set by a different domain than the website the user is visiting. |
| Access | Only accessible by the website that set them. | Accessible by the third-party domain that set them. |
| Purpose | Primarily for enhancing user experience (e.g., session management, preferences). | Primarily for tracking, advertising, and cross-site analytics. |
| Duration | Can persist between visits, depending on the setting. | Typically persistent, tracking users across multiple websites. |
| Privacy Impact | Considered less invasive since data is stored locally for a single website. | Can be more invasive since they track users across various sites, often without explicit consent. |
With evolving privacy concerns and regulations, staying updated on first-party and third-party cookies is crucial for businesses.
Businesses relying on third-party cookies for tracking and advertising must adapt to increasing browser restrictions and comply with global data privacy laws. On the other hand, first-party cookies offer businesses a way to maintain valuable user insights while respecting privacy and adhering to regulations.
Let’s take a deeper look at the privacy implications.
Also read: Differences Between First-Party and Third-Party Cookies and How to Set Them Up
Privacy Implications and Browser Changes
As concerns about online privacy have grown, third-party cookies have come under scrutiny. Third-party cookies are often used for tracking users across different websites, which raises concerns about data privacy and user consent. In response to these concerns, major web browsers, such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Apple Safari, have taken steps to limit or block third-party cookies by default.
- Safari: Apple’s Safari browser has implemented Intelligent Tracking Prevention (ITP) to block third-party cookies and limit cross-site tracking, even if the user hasn’t opted out of cookies.
- Firefox: Mozilla Firefox blocks all third-party cookies by default through its Enhanced Tracking Protection (ETP) feature.
- Chrome: In July 2024, Google announced a shift in its approach to third-party cookies. Instead of phasing them out entirely, Chrome now offers users the ability to make an informed choice regarding third-party cookie usage through existing privacy settings. This change was influenced by industry feedback and regulatory considerations. Google continues to support the Privacy Sandbox initiative, which affects how advertisers can target users across the web.
Regulations on Cookies and Data Privacy
In addition to browser changes, privacy regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) have made it more difficult to use cookies without user consent. These regulations require websites to obtain explicit consent from users before setting cookies, especially third-party cookies.
- GDPR: Under GDPR, websites must inform users about the use of cookies and give them the option to opt-in or opt-out of cookie tracking. Failure to comply can result in significant fines.
- CCPA: The CCPA requires businesses to disclose the types of data they collect, including data collected via cookies, and to give California residents the right to opt-out of the sale of their data.
Amid growing privacy concerns, Ingest Labs enables businesses to enhance their data strategies by prioritizing privacy-compliant, first-party data solutions. By leveraging first-party data through tools like Ingest ID and Ingest IQ, you can continue to deliver personalized experiences and maintain privacy compliance while staying ahead of the curve.
Also read: Understanding Cookie Size Limits in Modern Browsers
Conclusion
The debate between first-party vs third-party cookies is at the heart of many of today’s privacy conversations. First-party cookies provide valuable insights for improving user experience and website functionality, while third-party cookies have become a tool for extensive cross-site tracking and targeted advertising.
As privacy regulations evolve and browsers change their policies, it’s important for businesses to adapt their cookie strategies. By understanding the differences between first-party and third-party cookies and how they are regulated, you can make informed decisions that respect user privacy while still achieving your marketing goals.
Ingest Labs assists businesses in effectively adapting to changing regulations with precision. Our solutions, Ingest IQ and Ingest ID, enable you to collect valuable first-party data, maintain privacy compliance, and optimize user engagement without relying on third-party cookies.
Ready to future-proof your data strategy? Contact Ingest Labs today to discover how we can help you adapt to a cookieless world while maximizing your marketing efforts and staying compliant.
FAQs
1. What are first-party cookies used for?
First-party cookies are primarily used for improving user experience by remembering preferences, managing sessions, and collecting data for analytics on the website the user is visiting.
2. How do third-party cookies differ from first-party cookies?
Third-party cookies are set by domains other than the website a user is visiting and are mainly used for tracking across multiple sites, primarily for advertising and analytics purposes.
3. Are third-party cookies blocked in browsers?
Yes, many browsers, including Safari and Firefox, have started blocking third-party cookies by default due to privacy concerns.
4. What are the privacy implications of third-party cookies?
Third-party cookies can track users across different websites, raising concerns about user privacy and consent. This has led to stricter regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
5. How can businesses comply with privacy regulations regarding cookies?
Businesses must inform users about the cookies being used and obtain explicit consent, especially for third-party cookies. They must also respect users’ rights to opt-out or manage cookie preferences.