Think about how your marketing data travels inside your organization. You know the destination is revenue growth, but the path includes many signals, handoffs, and points of friction that affect outcomes.
Each individual interaction a prospect or customer has with your brand, an ad click, a site visit, a checkout event, forms a customer journey. These moments reveal intent, drop-off risk, and optimization opportunities at a granular level. When you zoom out, those individual paths combine into the customer lifecycle. This broader view reflects how accounts move from awareness to conversion, retention, and long-term value. It focuses on stages, timing, and progression rather than isolated touchpoints.
This guide explains the practical differences between customer lifecycle vs customer journey, why both matter for modern marketing teams, and how accurate, first-party data helps you turn fragmented interactions into measurable business outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- The customer lifecycle focuses on predictable stages from acquisition to advocacy, while the customer journey captures the actual path customers take across touchpoints.
- Customer lifecycle stages remain consistent across your business; journeys vary significantly based on customer segment, channel, and behavior.
- Privacy-compliant tracking solutions help you map both approaches without violating GDPR, CCPA, or regional regulations.
- Integrating lifecycle and journey data creates accurate attribution models that reduce ad spend waste.
- Common challenges like data siloes and attribution errors are significantly reduced when you unify customer data on a server-side platform.
What Is the Customer Lifecycle?
The customer lifecycle describes the predictable progression customers move through as they interact with your business over time. It's a framework that divides customer relationships into distinct stages, each with specific objectives and characteristics.
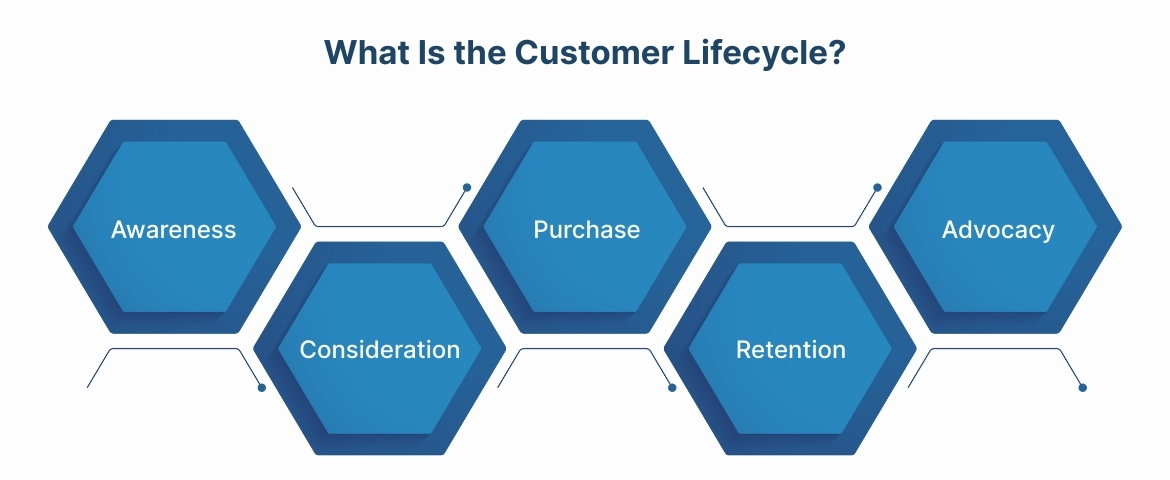
Your customer lifecycle typically includes five core stages:
- Awareness is where potential customers first discover your brand, products, or services. This stage involves marketing activities like content creation, paid advertising, and social media outreach.
- Consideration begins when prospects recognize a problem your business solves. They evaluate your offering against competitors and gather information to make an informed decision.
- Purchase is the transaction point where a prospect becomes a customer. This involves removing friction from checkout, offering incentives, or simplifying the buying process.
- Retention focuses on keeping existing customers engaged and satisfied. Your goal is reducing churn and encouraging repeat purchases through excellent service and ongoing communication.
- Advocacy represents your most valuable customers who actively recommend your business to others. These customers become brand ambassadors and generate referrals.
The customer lifecycle remains relatively static across your organization. Every customer follows these stages, though the time spent in each varies dramatically. For e-commerce brands, the purchase stage may take days. For B2B software companies, it might take months or years.
Why your business should care: Understanding lifecycle stages helps you forecast customer value, plan marketing budgets by stage, and identify where customers drop off. When you recognize that a customer is stuck in the consideration stage, you can adjust messaging to move them toward purchase. Server-side tracking platforms give you the data accuracy needed to identify these patterns without guessing.
What Is the Customer Journey?
The customer journey captures the actual sequence of touchpoints and experiences a specific customer experiences as they interact with your business. Unlike the lifecycle, which is predictable and staged, the journey reflects real behavior across channels, devices, and time.
A customer's journey typically includes multiple touchpoints. They might discover your brand through a Google search, visit your website, leave without purchasing, see a retargeting ad on social media, click through to your product page, read customer reviews, add items to their cart, and finally complete a purchase. Each interaction is part of their unique journey.
Several factors shape individual journeys:
- Channel diversity means customers interact with your brand across email, social media, your website, mobile apps, paid ads, and organic search. Their path isn't linear.
- Device switching complicates tracking because customers often start researching on mobile, continue on desktop, and purchase on tablet. Attribution becomes difficult without proper tracking infrastructure.
- Timing variations mean some customers journey from awareness to purchase in hours, while others take weeks or months to decide.
- Behavioral differences create unique paths based on customer interests, needs, and preferences. Two visitors to your homepage may take completely different routes.
- Mapping the customer journey gives you insight into which touchpoints drive conversions, where customers abandon, and which channels deserve more investment. A customer journey map shows what actually happened, not what you expected to happen.
Why your business should care: Journey maps reveal friction points costing you revenue. If you notice 40% of customers abandon after viewing pricing, that's actionable insight. If retargeting ads have higher conversion rates than organic search for a specific audience segment, you can optimize spending. Real-time journey tracking across web and mobile applications ensures you capture every interaction accurately.
Ingest Labs supports GDPR- and CCPA-aligned data collection through consent-aware, server-side tracking.
Understanding both concepts independently is useful, but the real clarity comes from seeing how they differ side by side.
Customer Lifecycle vs. Customer Journey: What's the Difference?
Your marketing team tracks customer behavior across channels, but do you know the real difference between customer lifecycle vs customer journey? Many businesses mix these terms and lose clarity on which data drives revenue. This section breaks down the distinction so you can apply both frameworks effectively in your operations.
Predictable Stages vs Individual Paths
- Customer Lifecycle: Your customers move through fixed stages (awareness, consideration, purchase, retention, advocacy) that apply to everyone. Use this for long-term planning and budgeting across your entire customer base.
- Customer Journey: Each customer follows a unique sequence of touchpoints across devices and channels. Track this to optimize specific interactions and reduce friction points.
Long-term Strategy vs Real-time Tactics
- Customer Lifecycle: Focuses on overall relationship progression over months or years. Your e-commerce team uses it to forecast lifetime value and allocate retention budgets.
- Customer Journey: Captures short-term interactions from first ad click to purchase completion. Agencies rely on journey data to adjust campaigns daily based on performance.
Business Perspective vs Customer Experience
- Customer Lifecycle: You define stages based on business goals and revenue milestones. This guides your team's quarterly planning and resource allocation.
- Customer Journey: Maps actual customer actions, emotions, and drop-off points. Privacy-compliant tracking reveals why 68% of carts get abandoned before checkout.
Aggregate Data vs Individual Sequences
- Customer Lifecycle: Analyzes patterns across thousands of customers to identify stage progression rates. Your finance team needs this for accurate revenue projections.
- Customer Journey: Examines single customer paths to pinpoint high-value sequences. Marketing managers use journey insights to shift ad spend from underperforming channels.
Static Framework vs Dynamic Behavior
- Customer Lifecycle: Stages remain consistent regardless of channel or device. Your operations team builds processes around these predictable milestones.
- Customer Journey: Changes based on customer behavior, timing, and preferences. Server-side platforms capture complete journeys across web, mobile, and apps.
Your business gains the most value when both frameworks work together. Customer lifecycle sets your strategic direction while customer journeys provide the tactical data needed for execution. Without accurate tracking across both, you risk misallocating budgets and missing optimization opportunities.
| Aspect | Customer Lifecycle | Customer Journey |
| Scope | Complete relationship from first contact to advocacy | Specific interactions during purchase or engagement |
| Timeframe | Months to years across multiple purchases | Hours to days for single transactions |
| Data Focus | Aggregated patterns for all customers | Individual touchpoint sequences |
| Primary Use | Annual planning and forecasting | Campaign optimization and personalization |
| Consistency | Fixed stages apply universally | Varies by customer segment and channel |
| Tech Needs | Basic analytics platforms | Server-side tracking + CDP integration |
Once the distinctions are clear, the next step is deciding which framework deserves more attention based on your business priorities.
How to Choose the Most Relevant Approach for Your Business?
Your business might benefit from one approach more than the other depending on your specific goals, business model, and current challenges. Here's how to decide which framework to prioritize.
Choose the customer lifecycle approach if:
- Your primary challenge is long-term business planning and forecasting. You need to understand average customer value, typical time-to-purchase, and retention rates. Large enterprises often use lifecycle analysis to report to shareholders on customer acquisition cost and lifetime value metrics.
- You're launching new market segments or product lines. Lifecycle data shows you how quickly different segments move through stages, helping you set realistic revenue targets and marketing budgets.
- You have limited data infrastructure. Lifecycle analysis works with basic analytics platforms and doesn't require sophisticated tracking or real-time data synchronization.
Choose the customer journey approach if:
- Your immediate priority is reducing cart abandonment, improving conversion rates, or increasing customer retention. Journey mapping pinpoints exactly where customers drop off and why.
- You operate across multiple channels and devices. E-commerce brands, digital agencies, and SaaS companies need journey mapping to understand how customers switch between touchpoints.
- You want to optimize ad spending and reduce wasted budget. Journey maps show which channel combinations drive conversions, helping you shift spending away from underperforming channels.
- You're building personalization and marketing automation strategies. Effective personalization depends on understanding individual customer journeys, not just aggregate lifecycle patterns.
Both frameworks serve your business, but timing matters. Start with customer journey mapping to fix urgent revenue leaks. Shift to lifecycle analysis once your tracking infrastructure captures reliable data patterns. Your choice reflects current pain points, not theoretical perfection. Ingest Labs helps unify both approaches through server-side tracking that activates quickly without rebuilding your existing stack.
Even with the right framework, execution breaks down when data, attribution, or privacy controls fall short.
How to Integrate Customer Lifecycle and Customer Journey Approaches?
Combining both frameworks creates a comprehensive customer understanding that individual approaches can't achieve alone. Integration means your lifecycle stages connect with actual customer journeys, revealing which interactions drive customers through each stage.
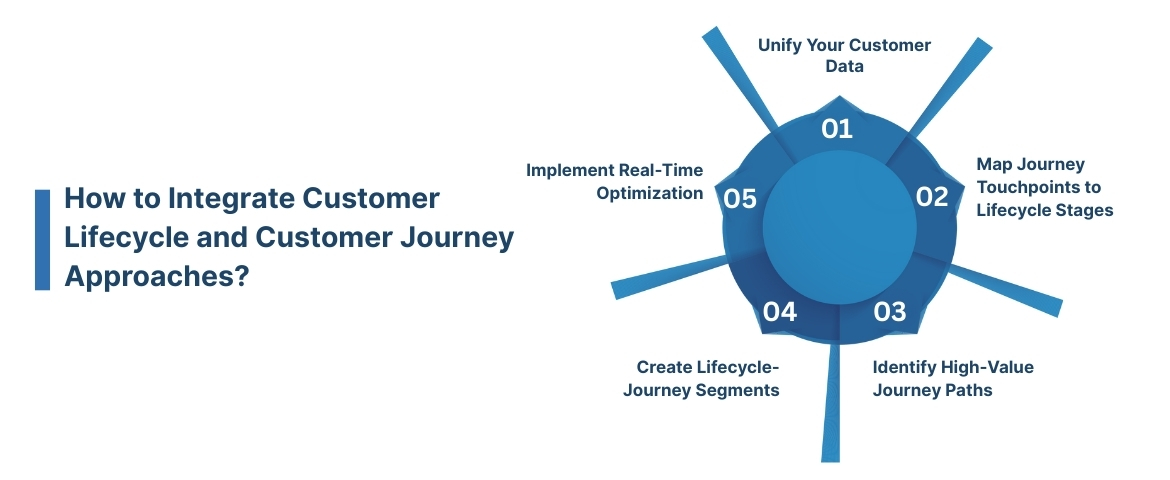
Step 1: Unify Your Customer Data
Start by connecting all customer interactions into a single source of truth. Your customer data platform should sync information from your website, mobile app, email platform, CRM, and advertising channels. When customer data remains siloed across systems, you can't accurately map either lifecycle stages or journey paths.
This is where server-side tracking becomes essential. Browser-based tracking misses interactions when customers use ad blockers or switch devices. Server-side platforms capture every event regardless of privacy settings, giving you complete journey visibility while maintaining GDPR and CCPA compliance.
Step 2: Map Journey Touchpoints to Lifecycle Stages
Assign each journey touchpoint to the appropriate lifecycle stage. A customer's first Google search is an awareness touchpoint. Their visit to your pricing page is consideration. This mapping shows you which channels and messages drive stage progression.
For example, you might discover that email engagement strongly correlates with moving customers from consideration to purchase. But social media performs better for awareness-stage prospects. This insight changes how you allocate marketing budget across channels.
Step 3: Identify High-Value Journey Paths
Not all customer journeys are equal. Some paths convert at 15%, while others convert at 3%. Analyze which combinations of touchpoints lead to highest-value customers. Maybe customers who see your brand in organic search, then click a retargeting ad, then read a case study have 40% higher lifetime value than customers who come from paid search alone.
This data informs your marketing strategy. You increase spending on the channels that lead to the highest-value journey sequences.
Step 4: Create Lifecycle-Journey Segments
Build customer segments based on both their current lifecycle stage and their journey history. Instead of generic "consideration stage" segments, create segments like "Consideration stage customers who visited pricing three times" or "Retention stage customers who engaged with email twice this month."
These precise segments enable personalized messaging that addresses specific customer needs and behaviors.
Step 5: Implement Real-Time Optimization
Use your integrated data to optimize experiences in real time. When a customer takes a journey sequence that historically predicts high-value purchase behavior, trigger targeted follow-up communications. When a customer enters a high-abandonment journey pattern, intervene with personalized offers or support.
Real-time optimization requires robust tracking infrastructure that captures every event instantly and processes it through your marketing automation platform without delay.
To connect journeys to lifecycle movement in real time, Ingest Labs synchronizes events, identity, and activation across your CDP and marketing stack.
Even with the right framework, execution often breaks down due to data gaps, attribution blind spots, and compliance constraints.
Common Challenges and How to Avoid Them
Most businesses encounter specific obstacles when managing either customer lifecycle or journey frameworks. Recognizing these challenges and knowing solutions prevents costly mistakes.
Challenges in Managing the Customer Lifecycle
- Data quality gaps: Customers shift stages unpredictably. Missed re-engagements or pauses distort lifecycle insights. Use strict stage rules and frequent audits to keep data accurate.
- Attribution complexity: Many touchpoints influence progress, yet last-click models hide early impact. Multi-touch attribution with first-party identifiers tracks influence without cookies.
- Inconsistent segmentation: Teams define stages differently, causing reporting conflicts. Standardize definitions and enforce one system of record.
- Long data lag: Monthly reviews delay action. Real-time lifecycle dashboards surface stalled customers when intervention still works.
Challenges in Managing the Customer Journey
- Multi-device attribution gaps: You see fragmented journeys when customers switch devices. Server-side, first-party tracking connects interactions into one continuous business view.
- Privacy and governance pressure: You must respect GDPR, CCPA, CPRA, and Canadian consent rules without losing visibility. Compliant server-side controls protect data and trust.
- Hidden cart abandonment causes: You only see the exit, not the path. Full event tracking exposes checkout friction versus product or pricing issues.
- Limited real-time action: You recognize high-intent patterns but cannot act fast. Automated triggers activate messages and offers instantly at scale.
- Disconnected data systems: Analytics, CRM, and marketing tools stay isolated. Unified customer profiles reveal which touchpoints actually drive revenue.
Final Thoughts
Customer lifecycle and customer journey are not competing frameworks; they solve different problems at different levels. The lifecycle gives you structure for planning, forecasting, and growth strategy, while the journey reveals where real customers hesitate, convert, or drop off. When these views remain disconnected, teams misread performance and waste budget fixing the wrong issues.
The real advantage comes from unifying both with accurate, privacy-compliant data. Ingest Labs enables this by capturing complete journeys server-side and mapping them reliably to lifecycle stages. If your growth decisions depend on fragmented tracking, contact Ingest Labs to see how a stronger data foundation turns insight into measurable outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is the customer lifecycle the same as the customer journey?
No, the customer lifecycle defines predictable stages customers pass through over time from acquisition to advocacy. The customer journey shows the actual sequence of touchpoints each customer experiences across channels and devices.
2. Which is more important for my e-commerce business: lifecycle or journey?
Customer journey matters most for e-commerce because it reveals friction that directly affects conversions and revenue. Lifecycle data adds value by showing where customers stall or progress over time.
3. How do I reduce cart abandonment using customer journey data?
Map every step from product view to checkout to identify where abandonment occurs most frequently. Compare completed purchase journeys with abandoned ones to pinpoint friction and optimization opportunities.
4. How do I map customer journeys across mobile apps and websites?
Standard analytics separates app and web behavior, creating fragmented customer views. First-party identifiers connect interactions across platforms into one continuous journey.
5. What's the difference between customer lifecycle and customer lifetime value?
Customer lifecycle explains progression stages, while customer lifetime value measures total revenue over the relationship. Customers who reach the retention and advocacy stages consistently generate higher lifetime value.
6. Should we use journey mapping for B2B sales or just B2C?
Journey mapping works well for B2B, even with longer sales cycles and multiple decision-makers. It reveals which behaviors and touchpoints signal sales readiness at each stage.