B2B buying is shifting fast. Economic pressure and digital adoption are reshaping how companies evaluate products, while buyers expect consumer-level ease across every touchpoint. They explore independently, compare options across channels, and leave the moment the experience feels slow or unclear.
The numbers show how dramatic this shift has become. US B2B e-commerce is projected to reach $3 trillion by 2027, signaling continued investment in digital sales models. At the same time, buyers now use an average of 10 interaction channels throughout their decision process. This creates a complex path that moves between ads, content, trials, demos, sales conversations, and product touchpoints.
Without visibility into this path, attribution breaks, friction grows, and teams miss the signals that influence conversions. Customer journey mapping gives B2B teams a clear structure for these interactions. It helps marketers, SaaS companies, and agencies understand intent, remove roadblocks, and support the full lifecycle with accurate, privacy-ready data.
This guide explains how to build a complete journey map that reflects modern buyer behavior.
Key Takeaways
- B2B buying has shifted to a digital-first approach, creating longer, multi-stakeholder journeys that most tracking systems fail to capture.
- Accurate journey mapping requires first-party data, server-side events, consent-aware tracking, and unified profiles across marketing, product, and CRM.
- Modern buyers interact with many channels and expect self-guided evaluation, which makes internal assumptions unreliable without real behavioral data.
- A strong map helps teams spot friction, understand intent signals, and connect revenue outcomes to specific touchpoints across the full lifecycle.
What Customer Journey Mapping Means for B2B Teams
Customer journey mapping is a structured way to document how prospects move from first interaction to long-term customer status. It captures every touchpoint buyers experience across marketing, sales, product, and support.
For B2B teams, this provides a complete view of how accounts discover your product, evaluate solutions, compare competitors, request demos, engage with content, and move toward purchase.
In B2B environments, a journey map goes beyond tracking a single user. It can connect stakeholder activity when identifiers such as emails, CRM IDs, or role-based user accounts are available. It highlights decision-makers, influencers, technical evaluators, and procurement teams, showing how each group interacts with content or engages with sales.
With a complete, connected map, teams can fix gaps, improve conversion paths, and create consistent experiences across all ten or more channels buyers use during evaluation.
Why B2B Journeys Are Increasingly Difficult to Track
B2B buying paths have become longer, more nonlinear, and more crowded with touchpoints. Multiple stakeholders participate in each decision, and interactions span ads, content, demos, trials, and product experiences. This complexity makes it hard for teams to understand what shaped intent, what slowed momentum, and what converted the account.
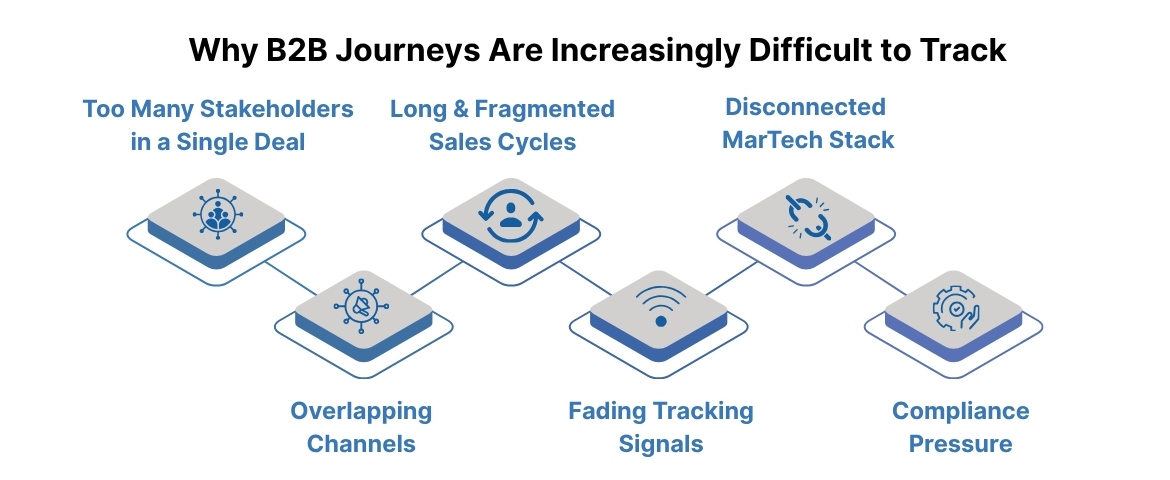
Tracking these interactions is even harder because traditional data signals are disappearing. Third-party cookies no longer work, device identifiers are unreliable, and script-based analytics fail when buyers block trackers. As a result, most teams operate with partial visibility, disconnected systems, and inconsistent attribution.
1. Too Many Stakeholders in a Single Deal
A B2B purchase rarely involves one person. Research shows that an average deal includes roughly 5 to 11 stakeholders with different roles and expectations. Aligning these interactions inside one journey view becomes difficult when each stakeholder triggers different signals across multiple channels.
2. Overlapping Channels and Nonlinear Touchpoints
B2B buyers interact with a wide range of channels during evaluation. A typical deal involves dozens of touchpoints across ads, email, content, webinars, product pages, sales calls, and trial environments. This makes it challenging to identify which steps influenced the decision and where friction occurred.
3. Long and Fragmented Sales Cycles
B2B cycles often stretch across months. Complex SaaS deals may span several quarters, and even mid-market cycles often exceed two hundred days from first touch to revenue. Most analytics setups lose accuracy over this duration, especially when buyers switch devices or clear cookies.
4. Fading Tracking Signals and Script Blockers
Third-party cookies are deprecated, device-level identifiers lack reliability, and browser privacy rules limit what marketers can capture. Form submissions, demo requests, and trial activations break when client-side scripts fail to load.
5. Disconnected MarTech Stack
CRM, ads, analytics, email, demo tools, and product usage systems often operate in silos. Without a shared data layer or unified identifiers, these tools cannot build a complete journey. As a result, teams track events, but not the buyer behind them.
6. Compliance Pressure and Non-compliant Data Flows
Many companies still depend on client-side tracking tools that do not meet modern privacy standards. Stitching data between tools without proper consent or governance introduces compliance risk and breaks journey continuity.
Want to capture significantly more touchpoints even when scripts fail? See how Ingest Labs strengthens your B2B journey data with server-side tracking and first-party identifiers. Contact our team to learn more.
Key Stages of the B2B Customer Journey
The B2B customer journey moves through several stages that reflect how prospects discover your product, evaluate its value, and continue to grow after becoming customers. Each stage includes specific behaviors, signals, and touchpoints that guide how teams design campaigns, track intent, and improve revenue outcomes.

1. Awareness
Buyers discover your product through ads, search, social content, events, or partner referrals. In SaaS, this often includes landing page visits, content interactions, and early brand exposure.
2. Consideration
Prospects begin comparing solutions. They explore feature pages, watch webinars, read case studies, and request resources that help them benchmark your SaaS product against alternatives.
3. Evaluation
Buyers look for hands-on validation. This includes free trials, sandbox access, demos, pricing reviews, and technical checks with product teams. These steps reveal serious intent.
4. Decision
The purchase moves through procurement workflows. Buyers navigate contracts, approvals, negotiations, and security reviews. For SaaS companies, legal and IT teams often join at this stage.
5. Onboarding
The customer implements the product. This includes account setup, user provisioning, integration steps, and migration. Smooth onboarding strongly influences long-term retention for SaaS teams.
6. Expansion
Once the product proves its value, customers explore add-ons, higher tiers, and new use cases. Product adoption metrics and usage insights trigger targeted upsell or cross-sell opportunities.
7. Advocacy
Satisfied customers share feedback through NPS surveys, reviews, and referrals. Strong advocacy helps SaaS companies build credibility and drive new pipeline without added acquisition cost.
These stages show how complex the path can become once multiple stakeholders and channels enter the picture. To make this complexity manageable, the next step is to convert real buyer behavior into a clear, structured journey map your teams can rely on.
Related: Basics of Customer Journey Orchestration
Build a B2B Customer Journey Map That Reflects Real Buyer Behavior
Buyer decision-making has shifted from sales-led motion to independent digital exploration. Most B2B buyers now complete a large part of their research without talking to sales, and by 2025, 80% of all B2B sales interactions will take place inside digital channels.
Buying preferences have permanently changed, meaning internal assumptions about the customer journey no longer align with actual behavior. Teams that follow an internal view of the funnel miss critical signals that happen across trials, demos, pricing pages, and product usage.
A reliable journey map starts with the outside-in perspective. It reflects what buyers actually do, not what teams believe they do. This requires first-party data, behavioral insights, conversations with customer-facing teams, and a clear structure for interpreting the signals that matter. The goal is simple: replace guesswork with evidence.
Below are the steps that help B2B and SaaS teams build an accurate, actionable journey map.
1. Clarify the Goal
Define what the map needs to solve. Some teams want cleaner attribution. Others want stronger trial activation, fewer drop-offs, or clearer ABM signals. A precise goal keeps the mapping focused and measurable.
2. Collect First-Party Data Across All Touchpoints
Use direct behavioral data to understand how buyers move through your funnel. This includes server-side website events, CRM activity, ad platform conversions, email and SMS interactions, support conversations, and product usage signals. First-party data grounds the map in reality.
3. Identify Key Buyer Personas
Map the roles involved across marketing, sales, procurement, RevOps, IT, and user groups. Each persona carries different expectations, approval power, and friction points. The map should reflect these differences without merging all roles into one view.
4. Map Intent Signals
List the actions that indicate interest or momentum. In SaaS, common signals include repeat pricing visits, POC requests, technical documentation views, and in-product activation steps. These signals show what buyers value and where they hesitate.
5. Define Success Metrics
Connect each stage to measurable outcomes. Typical metrics include pipeline creation, MQL-to-SQL conversion, demo-to-close rate, churn reduction, and expansion revenue. This ensures the journey map links directly to revenue performance.
6. Connect Systems
Ensure data flows across your CDP, CRM, marketing automation, analytics tools, and BI platform. Fragmented systems create blind spots and break the continuity of the journey. A unified data layer keeps every team aligned.
7. Visualize the Full Journey
Translate the data into a clear path that shows how anonymous visitors become identified leads, active evaluators, and paying customers. Dashboards or CDP journey views help teams spot friction points, identify drop-offs, and identify repeatable conversion patterns.
Also read: Track the Customer Journey Across Multiple Channels with Ingest Labs.
What Accurate Journey Mapping Requires
A useful journey map depends on more than documented stages and touchpoints. It needs reliable data, consistent identifiers, and a setup that captures how buyers behave across channels without losing accuracy to browser rules or tool limitations. The checklist below outlines the infrastructure that supports a complete and trustworthy B2B journey map.
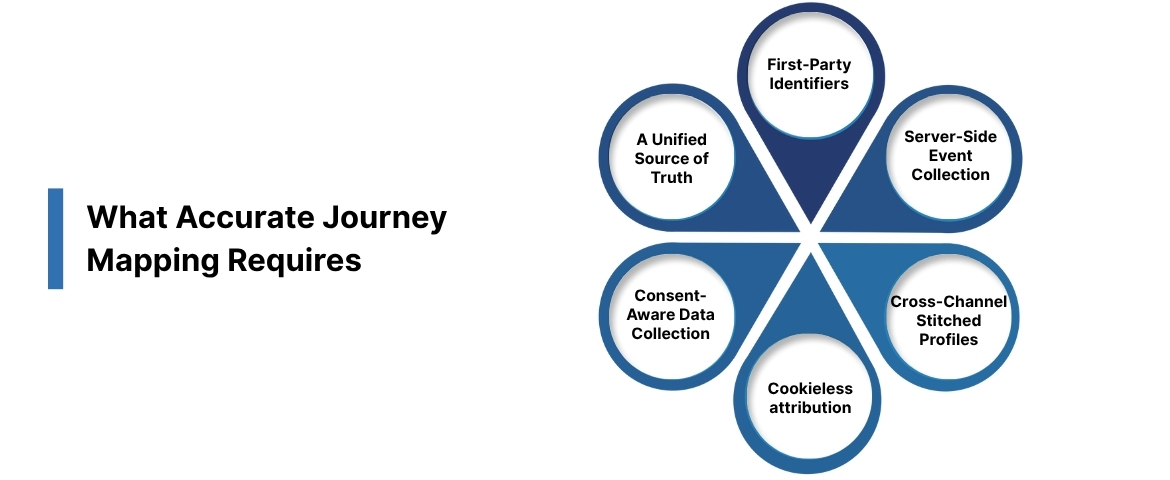
1. First-Party Identifiers
Use identifiers created and owned by your business rather than client-side identifiers that break when cookies are cleared. Link activity across sessions, devices, and channels when shared identifiers are present.
2. Server-Side Event Collection
Move critical tracking to the server layer to avoid gaps created by script blockers, browser limits, and inconsistent client-side execution. This keeps core signals intact and compliant.
3. Cross-Channel Stitched Profiles
Combine website activity, CRM events, product usage, and campaign interactions into a unified profile. This prevents fragmented views and helps teams understand how different signals contribute to the same account.
4. Attribution that is not solely Dependent on Cookies
Use conversion signals that remain accurate even when third-party cookies, device IDs, and pixel-based tracking fail. This is essential for modern B2B journeys with long cycles and multi-stakeholder paths.
5. Consent-Aware Data Collection
Ensure tracking respects preferences across all digital properties. A consent framework protects customer trust and keeps journey mapping aligned with privacy requirements.
6. A Unified Source of Truth
Give marketing, product, sales, and RevOps access to the same data foundation. A shared source of truth keeps teams aligned on which touchpoints matter, what drives conversion, and where friction appears.
Related:Essential Tools for Implementing Cross-Channel Marketing Automation
Final Thought
B2B journey mapping has become difficult because buyers move through long, multi-stakeholder paths across many digital channels while browser rules, tool silos, and disappearing identifiers limit what teams can track. Most organizations see only fragments of the journey, which leads to broken attribution, incomplete insights, and decisions guided by assumptions instead of evidence.
Ingest Labs supports this with three connected platforms that strengthen every part of the journey. Ingest IQ captures complete server-side events, so key signals never get lost. Ingest ID creates durable first-party identifiers that tie together anonymous sessions, lead activity, and account-level behavior. Event IQ can unify journey signals and revenue events when those systems are connected. Together, they give teams a clear, reliable picture of the whole B2B journey.
Ready to track the entire B2B customer journey with dependable accuracy? See how Ingest Labs strengthens your data in a privacy-first world. Book a demo to get started.
FAQs
1. Why is B2B customer journey mapping harder than B2C?
B2B journeys involve multiple stakeholders, long evaluation cycles, and interactions that happen across many channels. This creates fragmented signals that most tracking setups cannot capture cleanly, especially as browser rules limit client-side visibility.
2. What data do I need to build an accurate B2B journey map?
You need consistent first-party data from website activity, CRM events, product usage, marketing campaigns, and support interactions. Server-side signals help fill gaps caused by script blockers or cookie loss.
3. How does journey mapping support SaaS growth?
Journey mapping helps SaaS teams understand where trials stall, which touchpoints drive activation, and which signals predict conversion or churn. This guides product, marketing, and lifecycle decisions with evidence instead of assumptions.
4. How does Ingest Labs improve journey accuracy?
Ingest Labs provides server-side tracking, first-party identifiers, and unified customer profiles that combine marketing, product, and CRM data. This eliminates blind spots and gives teams a consistent view of the entire journey.
5. Can journey mapping support ABM programs?
Yes. A complete map shows how accounts engage across channels, which personas interact first, and which actions signal readiness. This helps ABM (Account-Based Marketing) teams prioritize accounts and personalize outreach with stronger intent data.