Sometimes analytics show healthy traffic, clicks, and conversions, but lurking under the surface, a large portion of that “traffic” isn’t even human. In fact, according to the 2025 Imperva Bad Bot Report, automated bots accounted for 51% of all global web traffic last year.
This isn’t a niche problem. Bots range from harmless crawlers to malicious actors wreaking havoc on ad spend, skewing analytics, and inflating engagement metrics. Without robust bot filtering, marketers risk making decisions on distorted data, wasting ad budgets, and missegmenting real human users.
This guide breaks down why bot filtering matters in 2026, where traditional tools fall short, and how teams can build a filtering strategy that protects data integrity without compromising user experience.
Key Takeaways
- Bot filtering removes non-human traffic to ensure analytics, attribution, and ad performance reflect real user behavior.
- Sophisticated bots mimic human behavior; multi-layered detection plus server-side validation improves accuracy.
- Filtering across all channels prevents inflated metrics, wasted ad spend, and missegmented audiences.
- Centralized bot management with cross-functional ownership ensures consistent, clean, and reliable data.
- Continuous monitoring and anomaly detection adapt to evolving bot patterns, keeping analytics trustworthy and actionable.
What Is Bot Filtering? A Simple Explanation
Bot filtering is the process of identifying, excluding, or routing non-human traffic so that analytics, attribution, and ad performance reflect real user behavior, not automated noise.
Unlike simple traffic metrics, bot filtering ensures that impressions, clicks, sessions, and conversions aren’t inflated by:
- scrapers and price crawlers
- credential-stuffing bots
- automated headless browsers
- ad fraud bots
- overly aggressive SEO or affiliate crawlers
For marketers, the danger isn’t just fraud, it’s the distortion of analytics. Bots create fake spikes in traffic, artificial scroll depth, inflated time-on-page, and false conversions that make it impossible to judge what humans actually engaged with.
Modern ecommerce sites see traffic coming from dozens of sources like ads, affiliates, SEO, apps, email, and each step is vulnerable to bot noise. Without proper filtering, teams lose visibility into:
- Which campaigns truly bring engaged users
- Whether page redesigns improved real behavior
- Whether a spike is human interest or bot scraping
- If retargeting pools are filled with actual shoppers
- How many sessions, clicks, and events come from genuine users
At its core, bot filtering helps brands answer:
- What percentage of traffic is actually human?
- Which pages or campaigns attract bot activity?
- Are analytics metrics inflated by non-human behavior?
- How much ad spend is being wasted on bots?
- Which security signals and behavioral patterns identify bots reliably?
Bot Filtering vs Bot Detection
Bot detection identifies whether traffic is or might be a bot. Bot filtering goes a step further: it decides what to exclude, include, segment, or route differently based on that detection.
Most marketers only focus on detection, looking at reports of bot traffic, but fail to implement filtering, which is what actually keeps analytics clean.
Here are the key differences between them:
| Aspect | Bot Detection | Bot Filtering |
| Purpose | Identify potential bots | Remove or segment bots from analytics |
| Output | Labels or risk scores | Clean data, filtered events, exclusions |
| Where it runs | Usually client-side or edge | Mostly server-side or data pipeline |
| Impact on analytics | Reports bot presence but doesn’t fix data | Ensures dashboards reflect only real users |
| Use cases | Security, monitoring, awareness | Accurate measurement, attribution, re-engagement |
Think of a metal detector at an airport. Detection is the beep that warns security. Filtering is the guard who actually stops the item from entering the gate.
Without filtering, the dangerous item still boards the plane, just like bots still pollute analytics even if you “detected” them.
Similar Read: Setting Up Offline Conversion Tracking in Google Ads
Now that you have a good understanding of bot filtering, let’s look at how it works.
How Bot Filtering Works
Bot filtering isn’t a single tool or script, it’s a multi-layered system that identifies non-human traffic using behavioral, technical, and environmental signals, then removes or reroutes those events before they distort analytics or attribution.
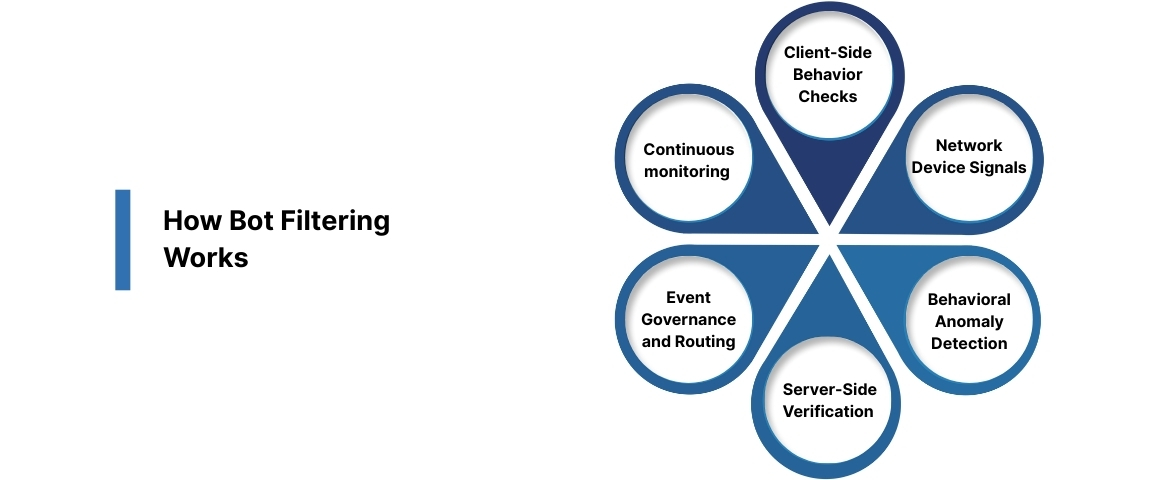
A mature filtering setup blends client-side checks, server-side validation, event governance, and ongoing monitoring.
1. Client-Side Behavior Checks
Client-side scripts run lightweight tests to understand whether a real user is interacting with the page. These tests include:
- Human interaction patterns: Mouse movement, idle time, scroll velocity, keystroke cadence, pointer curves. Bots tend to move in straight lines or fire events with robotic timing.
- Execution capabilities: Many bots don't execute JavaScript fully, fail on WebGL, or lack support for APIs like WebRTC or PerformanceObserver.
- Fingerprint consistency: Mismatched screen sizes, missing fonts, spoofed user agents, or impossible device/hardware combinations reveal automation.
- Touch and pointer signals: On mobile devices, real touch events generate micro-variations bots cannot mimic.
These signals quickly flag sessions that “look human but move like a script.”
2. Network-, Device-, and Infrastructure-Level Signals
Filtering systems also analyze technical metadata that bots can’t easily disguise:
- IP reputation: Known datacenter IPs, cloud-hosted VMs, and prior flagged IPs.
- ASN patterns: Residential traffic differs from AWS, DigitalOcean, or OVH traffic.
- TLS fingerprinting: Browsers generate unique TLS handshakes; bots often use outdated or mismatched ones.
- Proxy/VPN detection: High-risk proxy networks and rotating VPN pools introduce non-human volume.
- Headless browser detection: Tools like Puppeteer or Playwright leave predictable gaps (missing plugins, inconsistent rendering APIs, identical canvas fingerprints).
These infrastructure cues help distinguish genuine users from scripted sessions, even if the bot tries to mimic a browser.
3. Behavioral Anomaly Detection
This layer analyzes patterns over time, not just single sessions. Common anomalies include:
- Unrealistic navigation speed: 20 pages in 3 seconds, or scroll depth achieved instantly.
- Repeated URL sequences: Identical hit patterns across thousands of sessions.
- Evenly timed requests: Bots hit pages at perfectly regular intervals; humans behave irregularly.
- High-volume actions with no engagement: Pageviews but no clicks, scrolls, or gestures.
- Cold-start sessions: Bots often hit deep URLs without referral paths or previous sessions.
AI-based anomaly scoring is increasingly used to classify sessions at scale.
4. Server-Side Verification (the most reliable layer)
Server-side validation checks events once they are captured client-side, preventing untrusted traffic from entering analytics or ad systems. Server-side checks include:
- Origin validation: Confirming that the event originated from an allowed domain, SDK, or actual user browser.
- Signature checks: Verifying HMAC signatures or event hashes to prevent spoofed events.
- Sequence validation: Scroll event with no pageview? Purchase event with no cart? Bots often create impossible sequences.
- Rate limiting & deduplication: Ensuring only one valid event per milestone or action.
- Behavior merges: Connecting validated events with durable first-party identifiers to maintain continuity across sessions.
This layer ensures that even if client-side scripts fail or are blocked, bad traffic doesn’t corrupt downstream tools.
5. Event Governance, Cleanup, and Routing
Filtering is only complete when bot events are removed or quarantined before reaching analytics. This layer includes:
- Schema validation: Rejecting malformed or missing fields that bots often skip.
- Threshold validation: Logic that accepts scroll events only if preceded by minimum time-on-page or other human behaviors.
- Bot lists & allowlists: Adding internal tools, QA environments, and known crawlers to prevent accidental inclusion.
- Quarantine streams: Sending suspect traffic into a separate bucket (“bot_traffic”) for auditing instead of deleting it outright.
- Downstream routing rules: Ensuring GA4, Mixpanel, Amplitude, Meta, and Google Ads all receive human-only signals.
This is what keeps dashboards, ad audiences, and ROAS calculations from inflating artificially.
6. Continuous monitoring and drift detection
Bots evolve, and so must filtering. Real-time monitoring looks for:
- sudden traffic spikes from new ASNs
- scroll-depth events firing without scrolls
- hidden headless clusters
- mismatched browser + OS combinations
- anomaly increases after product releases or ad campaigns
- new scrapers hitting critical landing pages
This layer catches failures before they silently distort weeks of analytics.
Similar Read: What Data is Google Analytics Unable to Track
Now that you have a better idea of how bot filtering works, let’s explore why it’s essential for driving informed marketing decisions.
Why Bot Filtering Matters for Marketers
Bot traffic has become one of the biggest threats to accurate analytics, performance marketing, and attribution. As automation tools grow more sophisticated and browser restrictions limit traditional identity signals, bots now blend into human traffic more easily than ever. They inflate pageviews, break funnel metrics, pollute audience lists, distort campaign performance, and drain ad budgets without creating a single conversion.
Without reliable bot filtering, brands lose visibility into real customer behavior: abandoned carts appear higher than they are, conversion rates drop artificially, and retargeting pools fill with non-human sessions that waste spend. These distortions make it harder to optimize campaigns, measure ROI, or understand which channels genuinely drive revenue.
Here’s why bot filtering is essential today:
Maintain Data Accuracy Across Analytics
- Removes non-human events that inflate sessions, pageviews, and engagement.
- Prevents bots from polluting product analytics, funnel metrics, and dashboards.
- Ensures human behavior is measured without noise or artificial volume.
Protect Advertising and Attribution
- Eliminates waste by preventing bots from entering retargeting and lookalike pools.
- Reduces false clicks and impressions that inflate ad costs.
- Helps attribution tools evaluate true performance instead of corrupted traffic patterns.
Improve Re-Engagement and Personalization
- Ensures email, SMS, and push campaigns reach real users, not automated crawlers.
- Keeps lifecycle automation triggers tied to genuine shopper actions.
- Improves audience segmentation by filtering out invalid sessions.
Strengthen Site Security and Performance
- Blocks aggressive bots that scrape content, overload endpoints, or crawl at high frequency.
- Reduces server strain by preventing unnecessary requests.
- Improves site speed and availability for real visitors.
Future-Proof Measurement
- Works reliably even as cookies, IP addresses, and user-agent checks become less trustworthy.
- Relies on durable signals like behavioral analysis, server-side validation, and event governance.
- Supports first-party measurement strategies built around clean, human-only data.
Bot filtering isn’t just a hygiene step, it’s a foundation for accurate measurement, effective marketing, and efficient spend.
Want bot-filtered data that’s accurate, durable, and analytics-ready?
Ingest Labs helps brands remove bot traffic and maintain clean, reliable user data across all analytics and marketing platforms. By ensuring only human interactions are measured, marketers can trust their insights, optimize campaigns effectively, and make smarter decisions without noise or distortion.
Challenges of Bot Filtering (And How to Solve Them)
Bot filtering sounds straightforward, but accurately distinguishing human traffic from automated activity is complex. Sophisticated bots, proxy networks, and privacy restrictions often make traffic analysis noisy and unreliable. Without proper filtering, metrics like sessions, conversions, and engagement can be heavily skewed.
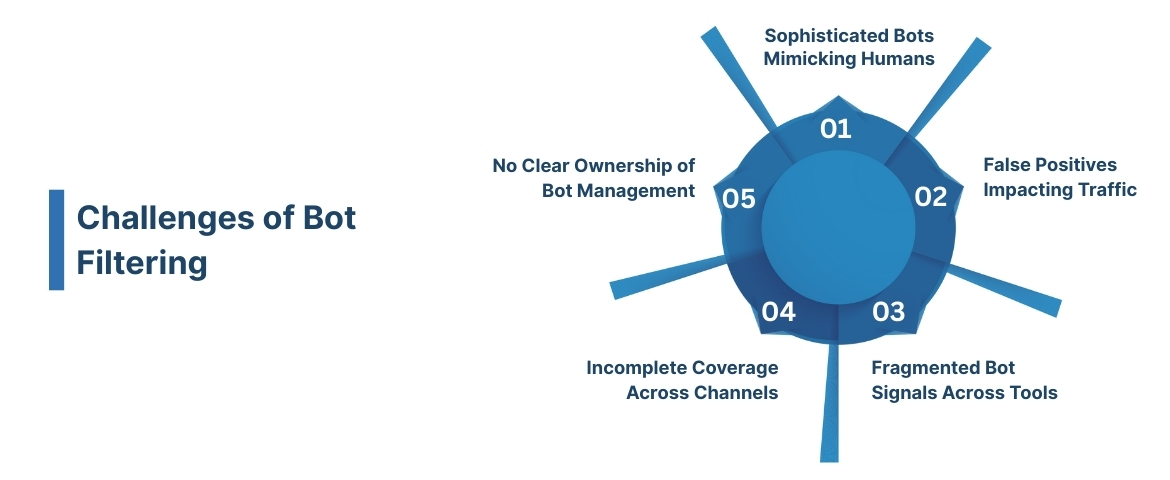
Below are the most common bot-filtering challenges and how to solve them effectively:
Sophisticated Bots Mimicking Humans
Modern bots emulate mouse movements, scrolling, clicks, and even form submissions, making them difficult to distinguish from real users. Some can bypass basic detection entirely, skewing traffic metrics and inflating engagement statistics.
Solution: Deploy multi-layered behavioral analysis, combining IP reputation, session timing anomalies, interaction patterns, and header inspection. AI-driven anomaly detection can flag traffic that deviates from human norms while continuously learning from new bot patterns.
False Positives Removing Legitimate Traffic
Aggressive filtering can unintentionally block actual users, resulting in missed conversions and underreported campaign performance. Over-reliance on simple rules like IP blacklists or high-frequency sessions can hurt legitimate analytics.
Solution: Use adaptive thresholds, monitor flagged traffic, and apply contextual verification before exclusion. Balancing strictness with flexibility ensures real users aren’t mistakenly filtered out.
Fragmented Bot Signals Across Tools
Different analytics, advertising, and personalization tools may classify bots inconsistently. For example, one platform may flag a traffic source as a bot, while another counts it as human. This creates unreliable reports and challenges for attribution.
Solution: Centralize bot filtering through a unified layer, applying consistent detection rules across all platforms. This ensures a single “source of truth” for clean, human-only traffic.
Incomplete Coverage Across Channels
Bots are not limited to web visits—they can appear in mobile apps, email click-throughs, or even API interactions. Partial bot filtering leaves gaps that distort cross-channel performance metrics.
Solution: Apply bot detection and filtering consistently across all touchpoints, including web, mobile, email, and API traffic. Layered approaches, like server-side filtering combined with client-side detection, capture the widest range of non-human interactions.
No Clear Ownership of Bot Management
Marketing, analytics, and engineering teams often assume someone else manages bot filtering. Without clear ownership, detection rules may become outdated, gaps persist, and analytics become unreliable.
Solution: Assign cross-functional responsibility for bot management. Document filtering rules, update them regularly, and implement automated monitoring. Proactive governance ensures ongoing accuracy and alignment with evolving bot behaviors.
Accurate bot filtering is critical for trustable analytics, proper attribution, and effective optimization. By standardizing detection, centralizing filtering, and enforcing governance, brands can rely on clean, human-only data to drive smarter decisions.
Related Read: Event Tracking Tools for Google Analytics
Conclusion
Bot filtering is one of the most critical yet overlooked aspects of accurate digital analytics. Without proper filtering, metrics can be inflated, engagement misinterpreted, and marketing decisions misaligned long before data reaches reporting tools.
Ingest Labs helps brands stabilize bot filtering through a unified event infrastructure. Ingest IQ ensures all interactions are accurately captured server-side, filtering out suspicious or duplicate traffic. Ingest ID maintains durable, first-party identifiers, so bot filtering is consistently applied across sessions and devices. Event IQ continuously audits event quality, flags anomalies, updates filtering rules, and keeps datasets clean and actionable.
Together, these processes turn bot management from a reactive task into a proactive, insight-ready framework that strengthens analytics, attribution, personalization, and ecommerce re-engagement strategies.
If you want clean, reliable traffic data and accurate reporting, Ingest Labs can help. Book a demo today.
FAQs
1. How can statistical modeling and machine learning refine bot filtering beyond static rules?
Modern bot filtering leverages machine learning to detect nuanced bot behavior patterns, using features like rapid-fire page visits, unusual navigation paths, or unexpected device combinations. Models can retrain on new bot signatures, flagging not just known bots but also novel, adaptive threats that rule-based filters might miss.
2. What challenges arise when filtering bots across multi-stage analytics pipelines?
In complex organizations, bot filtering must occur at several data collection, processing, and storage layers to ensure analytics accuracy and control costs. Early-stage filtering prevents pollution of analytics, but downstream logic may still need to flag bots for audits or exception handling as new patterns emerge.
3. How do advanced solutions distinguish between good bots (like search engine crawlers) and malicious or unwanted bots?
Bot management tools maintain updated databases of bot signatures and behaviors, cross-referencing user agents, IP ranges, and behavior telemetry to filter out only malicious and unidentified bots, while allowing legitimate bots crucial for SEO and integrations.
4. What approaches or tools exist for automated bot filtering in real time, and how do they scale?
Platforms like Spider AF or Statsig deploy real-time filters at the traffic edge, often using AI for live identification, tagging, and blocking. Solutions automatically update to match new threats and can integrate with ad networks or analytics to minimize wasted spend and data contamination.
5. What technical risks exist when relying solely on third-party bot filtering, and how can these be mitigated?
Third-party filters can lag in signature updates or falsely flag human users, leading to missed data or service disruptions. Combining external filters with in-house behavioral analysis and periodic manual audits ensures higher accuracy and resilience against evolving bots and accidental overblocking.