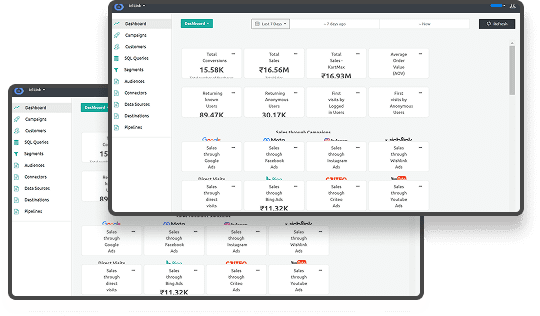
The rise of big data presents exciting opportunities and significant ethical challenges for us all in 2024. Harnessing vast datasets is crucial, but addressing privacy concerns and algorithmic biases is equally important. Therefore, data ethics is a huge necessity.
Data ethics is about doing the moral thing with data. It focuses on responsibly collecting, managing, and using personal and sensitive information. In this data-driven society, the ethical considerations surrounding data and its usage are becoming more prominent. This focus extends beyond legal compliance. It's essential for building trust and maintaining a responsible reputation with consumers and the broader public.
The Importance of Ethical Data Collection
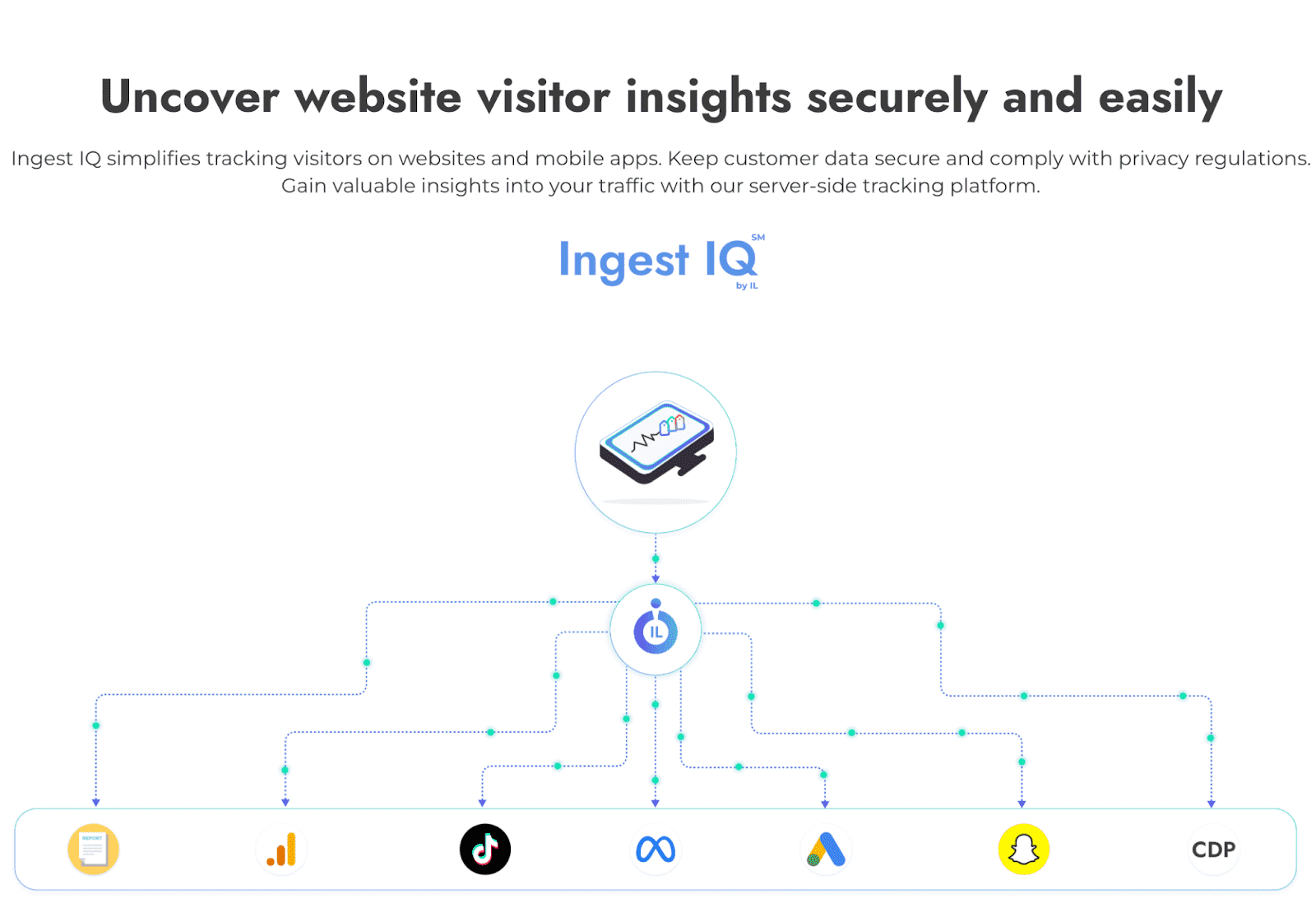
The significance of ethical data collection in today’s world cannot be overstated. As businesses and organizations increasingly rely on data to guide decisions, fuel innovation, and deliver customized services, the methods used to collect and implement this data carry substantial implications. Its importance is thus built on the foundation of the following attributes:
- Privacy, Trust, and Security of Customer Data
Access to vast volumes of data has profound implications for society. When you prioritize the security of customer information with privacy, you demonstrate a commitment to safeguarding their details against breaches and misuse. This, in turn, builds their trust. Thus, privacy, trust, and security are deeply intertwined.
- Legal compliance and Building Customer Trust
In the world of big data and advanced analytics, data ethics is an area that garners great demand from consumers. Legal compliance is crucial in building trust with your customers. Adhering to regulations shows that your business values privacy and respects the law. Check out how IngestLab adheres to ethical data practices.
- Corporate Responsibility
Corporate responsibility plays a vital role in building and maintaining customer trust. When a company prioritizes ethical practices, especially in handling customer data, it sends a clear message that it values its customers' privacy and security. Responsible data practices align with customers' expectations, reinforcing their loyalty and confidence in the brand.
Ethical Considerations: Build Customer Loyalty
Data ethics, within data collection and analysis, involves values and moral principles that direct how data is gathered, shared, and utilized. It requires respecting the rights and privacy of individuals whose data is being collected while ensuring transparency and fairness. Let’s look at the following ethical considerations:
- Information Security:
As the capacity to gather detailed personal information grows, respecting individual privacy becomes essential. Ethical data collection means securing consent, maintaining anonymity when needed, and communicating how data is used.
- Protecting Against Data Misuse:
Ethical standards are key to avoiding data misuse for discriminatory, exploitative, or manipulative purposes, particularly when handling sensitive information that could harm individuals.
- Social Accountability:
Ethical data practices embody a commitment to the broader impact of data on society, emphasizing the use of data not only within legal bounds but also in ways that enhance societal well-being.
Consent in Data Collection
Explicit data consent and informed data consent are related but not identical concepts. They are both critical in ethical data collection but focus on different aspects of the consent process. Let’s understand what consent in ethical data collection entails:
- Informed consent:
Informed consent is an individual’s voluntary agreement to participate in an evaluation where personal data is collected. This involves providing a clear statement outlining the evaluation’s goals, why the data is being collected, who will collect it, how it will be stored, for how long, and who will have access. As a data collector, you must ensure participants fully understand this information and provide informed consent.
- Explicit Purpose Consent and its Importance:
Explicit data consent requires the individual's clear and specific agreement to collect, process, or share their data. It’s often documented, such as through a signed form or a checkbox in a digital form. You need to communicate the specific reasons for data collection and how the information will be used. Without explicit consent, you risk undermining your process's integrity and your participants' privacy.
- Respecting User Rights and Voluntary Participation:
Voluntary participation is a key ethical guideline protected by international law and scientific codes of conduct. It ensures that participants join research willingly, free from external pressure or coercion. You must clarify that participants can leave the study at any time without needing to explain and without facing any negative consequences. Addressing ethical issues in data collection means maintaining this principle to protect participants' rights and uphold research integrity.
Ingest Labs provides businesses with tools to convey the data they collect, the reasons behind it, and how it will be utilized. This transparency is a regulatory requirement and a means to establish user trust.
Maintaining Anonymity and Confidentiality
Firstly, let us understand the difference between confidential and anonymous data. Confidential data includes personal information, such as medical or service details, that is kept private. On the other hand, anonymous data cannot be traced back to an individual. Both types are valuable.
Here are a few ways by which you could maintain anonymity and confidentiality with user data:
- Avoiding Collection of Personally Identifiable Information (PII):
A key ethical consideration in data collection is safeguarding the privacy of data subjects. Even with consent to collect and analyze personally identifiable information (PII), it doesn’t mean the data should be publicly disclosed. Storing data in a secure, centralized database is advisable to protect privacy. Implementing dual authentication and file encryption are effective measures to enhance data security. Ingest Labs supports these ideologies by allowing businesses to define specific purposes for data collection so unnecessary data is not collected.
- De-Identifying Datasets:
Complying with ethical issues in data collection involves ensuring that personal information is fully de-identified. This means removing all personal identifiers from the data to reduce the risk of re-identification and protect individual privacy. By following strict de-identification protocols, you can maintain data integrity while respecting privacy.
Ensuring Fairness and Avoiding Bias
It’s challenging to ensure that data collection methods are unbiased and truly reflect the diversity of populations. Here are a few ways by which you can combat this challenge:
- Preventing Harm and Ensuring Beneficence:
In ethical data collection, it's crucial to prioritize the well-being of individuals and communities. Preventing harm means considering the potential negative impacts of data use and taking steps to mitigate them. Ensuring beneficence involves using data to create positive outcomes that benefit the individuals whose data is collected and society. By carefully evaluating the potential consequences of data practices, you can help prevent harm and promote fairness.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance:
Adhering to legal and regulatory standards is essential to maintaining fairness and avoiding bias in data collection. Compliance with laws like GDPR and CPRA protects individuals' rights and ensures that data practices are transparent, accountable, and free from discriminatory outcomes. Staying up-to-date with evolving regulations is key to upholding ethical standards and building trust with those whose data you collect.
- Implementing Best Practices in Ethical Data Collection
Implementing best practices in ethical data collection means prioritizing transparency, privacy, and security at every step. By committing to these practices, you comply with regulations and build a stronger, more responsible relationship with your audience. Let’s read more about each of these:
- Protecting People’s Personal Data:
The core of data ethics is recognizing that personal information belongs to the individual. Collecting someone’s data without their consent is both illegal and unethical. To address ethical issues, you must obtain clear permission through signed agreements, digital privacy standards requiring acceptance of terms or cookie consent pop-ups. These practices ensure that users are fully aware of how their data will be used and give their authorization willingly.
- Right to Transparency and Accountability:
Individuals have the right to know how their personal information will be collected, stored, and used. Transparency and accountability are essential in handling data. For example, if a website tracks user behavior, users must be informed and given the choice to accept or decline cookies. Misleading or withholding information about data practices is unethical and illegal. To maintain trust, you must address data collection concerns upfront and ensure that your data practices are clear and honest.
- Robust Security Measures:
Implementing robust security protocols to safeguard collected data from unauthorized access, leaks, or breaches is essential. This involves using secure storage methods, encryption, and strict access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information.
Challenges in Ethical Data Collection
Carefully going through and addressing the complexities of ethical issues is essential. As you gather and analyze data, you face challenges like safeguarding privacy, preventing bias, and ensuring transparency. These challenges can impact trust and compliance, so addressing them head-on is crucial. Let’s look at a few of those challenges:
- Balancing Innovation with Privacy:
Striking the right balance between using data for innovation and protecting individual privacy can be challenging.
- Bias and Discrimination:
Data and algorithms can unintentionally reinforce biases and lead to discrimination if not managed carefully.
- Data Ownership and Control:
As data grows in value, questions about who owns and controls its use become more complex.
- Regulatory Compliance:
Going through the intricate web of data protection laws across various regions adds to the challenge.
Conclusion
Ethical data collection is a powerful tool for boosting customer loyalty. When you prioritize transparency and respect for privacy, your customers notice. They trust your brand more, knowing that their data is handled responsibly, which is crucial for long-term success. Compliance with ethical principles isn’t just about avoiding penalties; it’s about building a solid foundation for your business. It shows your commitment to doing the right thing, reinforces your brand’s integrity, and sets you apart from competitors.
Ingest Labs is committed to refining and advancing your approach to ethical data collection. Our robust solutions, featuring advanced tagging, real-time analytics, and privacy-focused tracking, ensure your marketing efforts thrive in the cookieless era. Ingest Labs is compliant to SOC 2 Type II, HIPAA, and GDPR. If you're ready to transform your programmatic advertising strategy, contact Ingest Labs today and upgrade your campaigns to new standards.